HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS is acquired immune deficiency syndrome. It is caused by HIV. The virus destroys the body’s immune system. This leaves a person unable to fight off diseases. The virus also attacks the central nervous system causing mental problems.
Signs & Symptoms
When first infected with HIV, many people have no symptoms. Within a month or two, some persons have flu-like symptoms (e.g., fever, fatigue, headache, and swollen glands). These symptoms usually go away within a week to a month. They are often mistaken for other infections. In adults, symptoms of HIV may take months to 10 or more years to appear. In children born with HIV, symptoms appear within 2 years.
Symptoms of HIV Before the Onset of AIDS
* Fatigue. Weight loss.
* Swollen glands.
* Fever and sweating. These occur often.
* Skin rashes that persist. Flaky skin.
* Getting sick often.
* Short-term memory loss.
* Infections. These include herpes, shingles, and yeast infections.
In Women, Signs that HIV Could be Present Include:
* Chronic vaginal yeast infections.
* Abnormal Pap test from HPV exposure in the past.
* Cervical cancer.
* Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
* Some sexually transmitted infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV). {Note: HPV can be present without HIV. Testing confirms its presence.}
AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV. With AIDS, there is a low level of cells in the blood called T4 cells. Persons with AIDS get many illnesses. These include skin infections, pneumonia, and cancer. These conditions are what lead to death.
Symptoms of AIDS
* Extreme fatigue. Weight loss.
* Severe and chronic diarrhea.
* Fever. Severe headaches.
* Shortness of breath. Coughing. A hard time swallowing.
* Abdominal cramps. Nausea. Vomiting.
* Lack of coordination. Vision loss.
* Mental status changes.
* Seizures. Coma.
Causes
HIV is spread when body fluids, such as semen or blood, pass from an infected person to another person. This includes having sex without a latex or polyurethane condom and/or sharing drug needles.
Infected females can give HIV to their babies during pregnancy, delivery, and breast-feeding. The risk of the baby getting HIV is greatly lowered if the mother takes antiviral medicines during the pregnancy and delivery. The baby takes medicine the first six weeks of life, too.
High Risk Activities for HIV Infection
* Anal, oral and/or vaginal sex without a latex or polyurethane condom, unless you limit sexual contact to one person and neither of you is infected with HIV. High risk situations are having sex:
– When drunk or high. (Judgement is impaired.)
– With multiple or casual sex partners or with a partner who has had multiple sex partners.
– With a partner who has used drugs by injection or is a bisexual male.
– When you or your partner has signs and symptoms of a genital tract infection.
* Sharing needles and/or “the works” when injecting any kind of drugs.
* Having had blood transfusions, especially before 1985, unless tested negative for HIV.
* Prolonged, open-mouth kissing with a person infected with HIV.
Blood screening tests are also done on donated blood which makes it highly unlikely that you’d get HIV from current blood transfusions. You cannot get HIV from:
* Donating blood.
* Casual contact, such as touching, holding hands, hugging, and dry kissing.
* A cough, sneeze, tears, or sweat.
* An animal or insect bite.
* A toilet seat. Using a hot tub or swimming.
Treatment
There is no cure for AIDS. Treatment includes:
* Medications. Multi-drug combinations are used.
* Measures to reduce the risk of infections and diseases (e.g., rest, proper nutrition, and vitamin supplements, as advised).
* Emotional support.
* Medical treatment for infections and chronic problems.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
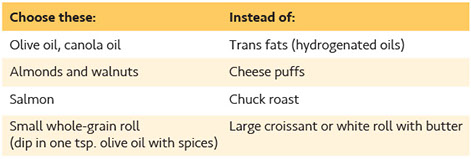
Someday, a cure for HIV/AIDS may exist. For now, prevention is the best protection. Take these steps:
* Unless you are in a monogamous relationship in which you and your partner are HIV free, use male latex or polyurethane condoms every time you have sex.
* Don’t have sex with people who are at high risk for HIV. These are:
– Persons with multiple sex partners.
– Persons who inject illegal drugs.
– Partners of persons infected or exposed to HIV.
– Persons who have had multiple blood transfusions, especially before 1985, unless tested negative for HIV.
* Ask specific questions about your partner’s sexual past (e.g., have they had many partners or unprotected (no condom) sex?). Ask if they have been tested for HIV and if the results were positive or negative. Be aware, though, that the response may not be an honest one. You need to protect yourself! Get tested for HIV. Ask your partner to get tested, too. If you have been exposed to HIV, use prevention measures or avoid sex until you get tested for it.
* If you’ve had sex with someone you suspect is HIV positive, see your doctor.
* Don’t share needles with anyone. This includes illegal drugs, such as heroin, as well as, steroids, insulin, etc.
* Don’t share personal items that have blood on them, such as razors.
* Plan ahead for safer sex. Decide what you’ll say and be willing to do ahead of time with a potential sex partner.
* Keep a supply of condoms handy (e.g., in your purse, by the bed, in your pocket, etc.). Know the correct way to use them. Putting the condom on your partner can be a part of foreplay.
* Don’t have sex when your judgement is impaired, such as while under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
* Avoid sex if either partner has signs and symptoms of a genital tract infection.
Detection
A rapid oral HIV test and blood tests detect antibodies to HIV. Get tested for HIV at doctors’ offices, clinics, and health departments or use a home test and counseling service, such as Home Access. You can buy this over-the-counter, by phone at 800.HIV.TEST (448.8378), or online atwww.homeaccess.com.
Resources
National AIDS Hotline
800.CDC.INFO (232.4636)
AIDS Info
800.HIV.0440 (448.0440)
www.aidsinfo.nih.gov