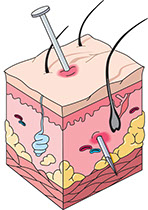
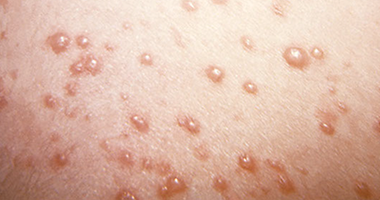
This is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. This condition is contagious.
Chickenpox
Signs & Symptoms
Flat, red spots that become raised and look like small pimples. These develop into small blisters that break and crust over. Fatigue and mild fever occur 24 hours before rash appears. Itching may be intense.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if it occurs in an adult; if self-care measures don’t bring relief in children; or if there are signs of infection (e.g., pus, increased redness, swelling, or pain). A vaccine is given to prevent this disease.
Self-Care
Keep from scratching affected areas. Apply cool, wet washcloths with baking soda or calamine lotion to affected areas. Take acetaminophen for fever. Take an OTC antihistamine as advised by your doctor if itching is intense. Chickenpox can be prevented with a chickenpox vaccine.
Contact Dermatitis
Causes are direct contact with poison ivy, oak, or sumac or contact with an irritant (cleaning product, cosmetic, jewelry, etc.).
Signs & Symptoms
Dry, red, itchy patches of skin. Blisters which may drain and then crust over.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if self- care measures don’t bring relief or if there are signs of infection (e.g., red streaks, fever, pus, increased redness, swelling, or pain).
Self-Care
Try to identify the irritant and avoid direct contact with it. Don’t scratch the rash. For itching, apply calamine lotion or OTC hydrocortisone cream to the affected area. Bathe in warm (not hot) water. Add an oatmeal product to the water. Pat (don’t rub) the skin dry. Take an OTC antihistamine as advised.
Cradle Cap
This is due to hormones that pass through the placenta before birth.
Signs & Symptoms
Scaly, crusty rash (in newborns) that starts behind the ears and spreads to the scalp.
What To Do
Use self-care.
Self-Care
Apply mineral oil to the scalp to soften the hard crusts, then use an antidandruff shampoo. Do this 2 to 3 times a week, massaging the scalp with a soft brush or washcloth for 5 minutes. Be sure to wash all of the oil out.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
This tends to run in families. It is common in persons with asthma or allergies. Contact with irritants may worsen eczema.
Signs & Symptoms
Patches of skin that are dry, red, scaly, blistered, swollen, and sometimes thick, discolored, or oozing and crusting. Commonly occurs in the bend of the elbow or behind the knee.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if self- care measures don’t bring relief or if there are signs of infection (e.g., red streaks, fever, pus, increased redness, swelling, or pain).
Self-Care
Use an OTC hydrocortisone cream on the affected area. Don’t scratch. Don’t bathe too often. When you do, use warm (not hot) water and a mild soap (or no soap). Use a light, nongreasy, unscented lotion (without alcohol) after you wash. Avoid items that worsen the eczema.
Heat Rash (Prickly Heat)
Heat rash (prickly heat) or chafing. This occurs from too much sweating.
Signs & Symptoms
Rash with small red pimples, pink blotchy skin, and itching. Common sites are between skin folds (armpits, under the breasts, the groin).
What To Do
Use self-care.
Self-Care
Bathe in cool water without soap every couple of hours. Let your skin air dry. Put cornstarch in body creases or apply calamine lotion to very itchy spots. Don’t use ointments and creams that can block sweat gland pores. Stay in a cool, dry area.
Fifth Disease
This is caused by the Human parvovirus B19. This condition is contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Red rash of varying shades that fades to a flat, lacy pattern. Rash comes and goes. It usually starts on the facial cheeks and then on the arms and legs. This is a mild disease, usually with no other symptoms.
What To Do
Use self-care, but no special treatment is required.
Self-Care
Avoid hot or even warm baths or showers. Keep cool.
Hives
Hives, usually due to an allergic reaction.
Signs & Symptoms
Red or pink, raised areas on the skin (weals) that can change shape, fade, then rapidly reappear. May come and go anywhere on the body. Itching.
What To Do
Call 9-1-1 if hives come with a hard time breathing or swallowing, wheezing, severe swelling all over or of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat (severe allergic reaction). {Note: If you have an emergency kit for an allergy, give the shot from the kit and follow other instructions before medical care.} For hives without a severe allergic reaction, see doctor for severe hives or for attacks of hives that recur.
Self-Care
Avoid substance that caused allergic reaction. Take an over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamine as advised by your doctor. Take a lukewarm (not hot) shower or bath. Add baking soda or an oatmeal bath product to bath water. Apply a cold compress or calamine lotion to itchy areas. Wear loose-fitting clothes. Don’t take aspirin, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, or naproxen sodium. Relax as much as you can.
Impetigo
This is caused by a bacterial infection. This condition is contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
In infants, pus-filled blisters and red skin. In older children, golden crusts on red sores. Areas affected are the arms, legs, face, and around the nose first, then most of body. Sometimes fever. Occasional itching.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider, especially if self-care measures don’t bring relief, if blisters are larger than 1 inch across, or if a red streak runs from the infection. An antibiotic may need to be prescribed.
Self-Care
Clean the area with an antibacterial soap several times a day. Apply an OTC antibiotic ointment 3 times a day after the scab falls off. Wash your hands after contact with the rash area. Don’t share towels, etc.
Lyme Disease
This is caused by a deer tick bite.
Signs & Symptoms
A fever and red rash 3 days to 2 weeks after a deer tick bite. The rash has raised edges with pale centers. It fades after a few days. Joint pain may develop later.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider for diagnosis. Can be treated with an antibiotic.
Self-Care
Follow your doctor’s advice.
Measles
This is caused by a virus. This condition is contagious. MMR vaccines prevent measles.
Signs & Symptoms
Blotchy red rash that starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. Rash lasts about 7 days. These signs come before the rash: Fever; runny nose; sneezing; cough; eyes that look red and are sensitive to light; and blue-white spots in the mouth.
What To Do
Call doctor right away to be sure the problem is measles. If it is, follow the doctor’s advice. Let the child’s school and the local health department know.
Self-Care
Rest until fever and rash go away. Drink lots of liquids. For fever, take acetaminophen. Treat cough. Avoid lights, TV, reading, etc. while eyes are sensitive to light. Usually okay to return to school about 7 to 10 days after rash and fever are gone.
Meningococcemia
Meningococcemia from a meningitis infection. These conditions are contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Rash of deep red or purple spots that don’t fade when the skin is pressed. Other symptoms include high fever; stiff neck; severe headache that persists; vomiting; lethargy; seizure; sensitivity to light; and bulging of the fontanelle (soft spot of the skull) in an infant.
What To Do
Get medical care fast!
Self-Care
After medical care, follow your doctor’s advice.
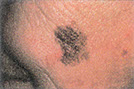
Psoriasis
This is a chronic skin disease that tends to run in families. The exact cause is not known.
Signs & Symptoms
Itchy, red patches covered with silvery-white flaky skin. Common sites are the scalp, elbows, forearms, knees, and legs.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if psoriasis affects large areas of skin and/or if self-care measures don’t bring relief.
Self-Care
To prevent dryness, use a moisturizer. Use an OTC hydrocortisone or coal tar cream or ointment. If psoriasis affects your scalp, use an antidandruff shampoo. Take a bath with mineral salts or an oatmeal bath product.
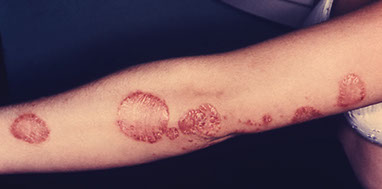
Ringworm
This is caused by a fungal infection. This condition is contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Redness, itchy, scaly patches on the skin or scalp that are round with distinct edges that grow outward as the infection spreads. Moistness in the folds of the skin (under the breasts or in the groin area). Bald spots may appear on the scalp.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider for diagnosis and treatment, especially if you have not had this before or if ringworm occurs on the scalp or in several patches on the skin.
Self-Care
Follow your doctor’s advice.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocky mountain spotted fever, 1 to 14 days after a bite from an American dog tick or Rocky Mountain woodtick. These conditions are contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Pink to red rash on the arms, legs, and palms of the hands. Often starts near the wrists and ankles, then spreads inward. Rash darkens in color, spreads, and can bleed. Sudden high fever with chills, severe headache, and delirium also occur.
What To Do
Contact doctor right away.
Self-Care
Follow your doctor’s advice.
Rosacea (Adult Acne)
The exact cause is not known. It may result from overuse of corticosteroid creams or alcohol use.
Signs & Symptoms
Red rash on the face. Red nose that looks swollen and puffy cheeks. May have pus-filled spots without blackheads or whiteheads.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if rosacea affects large areas of skin and/or if self-care measures don’t bring relief.
Self-Care
Avoid hot and/or spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine. Don’t rub or massage the face. Avoid strong sunlight.
Roseola
This is caused by the Herpes type-6 virus.
Signs & Symptoms
Flat, rosy red rash on the chest and abdomen. A high fever occurs 2 to 4 days before the rash. The child feels only mildly ill when the fever is present.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if high fever causes febrile seizure.
Self-Care
Take acetaminophen for fever. Apply cool, wet washcloths or take baths with tepid (not cold) water.
Scabies
This is caused by skin parasites called itch mites. This condition is contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Tiny red pimples that itch intensely, usually between the fingers, on the wrists and genitals; in the armpits; and along the belt line. Scabs and sores may form.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider for diagnosis. Can be treated with a prescribed topical medicine.
Self-Care
Follow your doctor’s instructions. Wash clothing and bedding in hot water and detergent.
Scarlet Fever
This is caused by a bacterial infection. These conditions are contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Rough, bright red rash (feels like sandpaper) on the face, neck, elbows, armpits, and groin. It spreads rapidly to entire body. A high fever and weakness occur before the rash. Other symptoms include sore throat, peeling of the skin, vomiting, and swollen tongue.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider for diagnosis. Can be treated with an antibiotic.
Self-Care
Take acetaminophen for fever. Rest and drink plenty of fluids.
Seborrhea
This is a type of dermatitis. The glands in the skin make too much oil.
Signs & Symptoms
Scaly, oily rash with small, reddish-yellow patches. Areas affected are usually oily ones (the edge of the scalp, forehead, nose, and eyebrows) and the back and chest.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider if self- care measures don’t bring relief or if there are signs of infection (e.g., red streaks, fever, pus, increased redness, swelling, or pain).
Self-Care
Use an OTC antidandruff shampoo with salicylic acid on the scalp area. Use OTC hydrocortisone cream on the affected skin areas. Handle the skin gently. Don’t scratch. Don’t use irritants like detergents.
Shingles
Shingles from the herpes zoster virus.* (Persons who have not had chicken pox or a vaccine for it can get chicken pox from exposure to shingles.) These conditions are contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Rash of painful red blisters (most often on only one side and in only one area of the body). Pain, itching, burning, or tingling feeling before the rash appeared.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider within 24 to 72 hours for an oral antiviral medicine. This can shorten the course of shingles and make symptoms less severe. {Note: All adults 60 years of age and older are advised to get a vaccine that can help prevent shingles and reduce the pain due to shingles.}
Self-Care
Take pain relievers as advised by your doctor. For itching, apply calamine lotion or a paste made of 3 teaspoons of baking soda mixed with 1 teaspoon of water to the affected area. Apply a cool, wet compress to blisters for 20 minutes at a time. Wash (don’t scrub) blisters until they crust over. Drink plenty of liquids.
Syphilis
This is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a specific bacterial infection. This condition is contagious.
Signs & Symptoms
Widespread red rash on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and sometimes around the mouth and nose. The small, red, scaly bumps do not itch. Other types of rashes, swollen lymph nodes, fever, and flu-like symptoms may also occur.
What To Do
See doctor or health care provider for diagnosis. Can be treated with an antibiotic.
Self-Care
Follow your doctor’s advice.
West Nile Virus
West Nile virus, 3 to 15 days after a bite from a mosquito infected with the virus.
Signs & Symptoms
Rash on the trunk of the body with fever, headache, bodyaches, and swollen lymph glands.
What To Do
See doctor right away.
Self-Care
Follow your doctor’s advice.