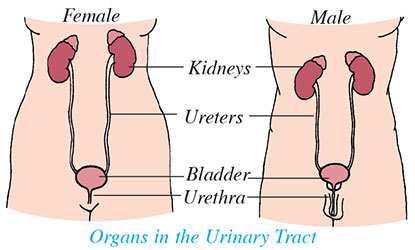
Common urinary problems in women are urinary incontinence, overactive bladder (OAB), and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Signs & Symptoms
Urinary incontinence means you lose bladder control or can’t store urine like you should. Although there are many types, the most common ones in women are stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
For Stress Incontinence
Urine leaks out with a sudden rise in pressure in the abdomen. This can occur when you cough, sneeze, lift, jump, run, or strain to pass stool.
For Urge Incontinence
Urine is released before you can get to the toilet due to a sudden and intense urge to urinate.
For Overactive Bladder
You urinate often (8 or more times during the day and at least 2 times during the night) and you have a sudden and urgent need to urinate.
For Urinary Tract Infections
Bladder Infection Symptoms
* You urinate more often than usual. It burns or stings when you urinate.
* Your urine is bloody or cloudy.
* You have pain in the abdomen or over your bladder.
* Confusion or other change in mental status, especially if you are over age 70.
Kidney Infection Symptoms
* Fever and shaking chills. Nausea and vomiting
* Pain in one or both sides of your mid back.
Sometimes, there are no symptoms with a UTI.
Causes & Risk Factors
For Urinary Incontinence
Problems occur with bladder muscles and nerves that help you hold or release urine and structures that support the bladder. This can be due to many factors:
* Physical changes due to aging or injury.
* Pregnancy and childbirth.
* Menopause.
* Multiple sclerosis.
* Spinal cord injury.
For Overactive Bladder
Abnormal nerves send signals to the bladder at the wrong time. This causes spasms in the bladder muscles to squeeze without warning.
For Urinary Tract Infections
Bacteria infect any part of the urinary tract – the kidneys, bladder, and ureters (tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder).
Treatment
For Incontinence:
* Bladder training, pelvic floor muscle training, or Kegel exercises.
* Medications.
* Medical treatment, such as an electric or magnetic stimulation device.
* Surgical procedures.
For Overactive Bladder
Medications that help relax muscles of the bladder and prevent bladder spasms.
For Urinary Tract Infections
An antibiotic is prescribed to treat the specific infection. Pain relievers are taken as needed.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
For Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
* Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day. Drink juice made from unsweetened cranberry juice concentrate. Take cranberry tablets.
* For pain, take acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, or Uristat®, an over-the-counter medicine for bladder infection pain.
* Wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting slacks.
* Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods.
For Urinary Incontinence
* Avoid caffeine. Limit or avoid fluids 2 to 3 hours before bedtime.
* Limit carbonated drinks, alcohol, citrus juices, greasy and spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners.
* Empty your bladder before you leave the house, take a nap, or go to bed.
* Try to urinate often, even if you don’t feel the urge. When you urinate, empty your bladder as much as you can. Relax for a minute and try to go again.
* Keep a diary of when you leak urine. If you do this every 3 hours, empty your bladder every 2 hours. Use an alarm clock or wristwatch with an alarm to remind you.
* Wear absorbent pads or briefs, as needed.
* Ask your doctor if your type of incontinence could be managed by using self-catheters. These help to empty your bladder all the way. A doctor needs to prescribe self-catheters.
Kegel Exercises
Kegel exercises are pelvic floor exercises. These help treat or cure stress incontinence. Follow these steps:
1. Start to urinate, then hold back and try to stop. If you can slow the stream of urine, even a little, you are using the right muscles. You should feel muscles squeezing around the anus and the urethra (the tube through which urine is passed).
2. Relax your body. Close your eyes. Imagine that you are going to pass urine and then hold back from doing so. You should feel the muscles squeeze like you did in step 1.
3. Squeeze the muscles for 3 seconds. Then relax them for 3 seconds. When you squeeze and relax, count slowly. Start out doing this 3 times a day. Gradually work up to 3 sets of 10 contractions. Hold each one for 10 seconds at a time. You can do Kegel exercises when you lie down, sit, and/or stand.
4. When you do these exercises do not: Tense the muscles in your belly or buttocks; hold your breath; clench your fists or teeth; or make a face.
5. Squeeze your pelvic floor muscles right before and during whatever it is (jumping, etc.) that causes you to leak urine. Relax the muscles once the activity is over.
6. You can also use pelvic weights prescribed by your doctor. You insert a weighted cone into the vagina and squeeze the correct muscles to keep it from falling out.
Do pelvic floor muscles daily. It may take several months to benefit from them. Get help to do them from:www.medicinenet.com/kegel_exercises_for_women/article.htm.
FYI: Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
Note: Symptoms of a condition called Interstitial Cystitis (IC) mimic those of an acute UTI. Intense pain and pressure in the lower abdomen come with the need to urinate. (This can be more than 50 times a day.) Nine out of 10 persons who have IC are women. Antibiotics do not give relief, because bacteria is not present with IC. This condition needs medical diagnosis and treatment.
Resources
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
www2.niddk.nih.gov
National Association for Continence (NAFC)
800.BLADDER (252.3337)
www.nafc.org