Ear, Nose & Throat Conditions
Signs & Symptoms
* Mild to severe ear pain.
* Feeling of fullness or discomfort in the ears.
* Tugging at the ear and restlessness in young children.
* Ear pain.
* Some hearing loss.
* Blood or other discharge from the ear (especially after sticking an object in the ear or exposure to extremely loud noise).
Causes
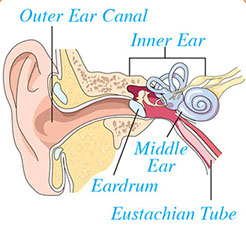
The most common cause of earaches is plugged Eustachian tubes. These go from the back of the throat to the middle ear. Fluid or pressure in a plugged Eustachian tube causes pain. This is caused by an infection of the middle ear, a cold or sinus infection, or allergies. Other things that can cause ear pain include changes in air pressure in a plane, something stuck in the ear, too much earwax, tooth problems, and ear injuries.
Treatment
Treatment includes pain relievers and methods to dry up or clear the blocked ear canal. Self-care can be used to treat many earaches. Severe and/or constant ear pain needs a medical diagnosis. Often, antibiotics are not needed for middle ear infections in children. About 8 in 10 children with ear infections get better without antibiotics. Let your child’s doctor decide if and when an antibiotic should be prescribed.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
To Help Prevent Ear Pain
* Don’t put cotton-tipped swabs, bobby pins, etc., in your ears. This could damage the eardrum.
* Don’t blow your nose with too much force.
* If you can, avoid places that have very loud noises (construction sites, etc.). Wear earplugs when exposed to loud noises.
* Keep the volume on low when using stereos, compact discs (CDs), etc. If someone else can hear the music when you are listening to one of these devices with earphones, the volume is too loud.
To Avoid Getting “Swimmer’s Ear”
* Wear wax or silicone earplugs.
* Wear a bathing cap.
* Don’t swim in dirty water. Swim on the surface not underneath the water.
* Use an over-the-counter product, such as Swim-Ear, as directed.
To Reduce Ear Pain
* Place a warm washcloth next to the ear. Some health professionals recommend putting an ice bag or ice in a wet washcloth over the painful ear for 20 minutes.
* Take an over-the-counter medicine for pain as directed on the label.
To Open Up the Eustachian Tubes and Help Them Drain
* Sit up. Prop your head up when you sleep.
* Yawn. This helps move the muscles that open the Eustachian tubes.
* Chew gum or suck on hard candy. (Do not give to children under age 5.) This tip is especially helpful during pressure changes that take place during air travel, but can also help if you wake up with ear pain.
* When traveling by air, stay awake when the plane takes off and lands. Wear ear plugs.
* Take a steamy shower.
* Use a cool-mist vaporizer, especially at night.
* Drink plenty of cool water.
* Gently, but firmly, blow through your nose while holding both nostrils closed until you hear a pop. This can be done several times a day.
* If okay with your doctor, take a decongestant to help relieve the swelling that causes the pain. (Don’t use a nasal spray decongestant for more than 3 days unless directed by your doctor.)
* When you give a baby a bottle, hold the baby in an upright position.
To Treat a Mild Case of “Swimmer’s Ear”
The goal is to clean and dry the outer ear canal without doing further damage to the top layer of skin.
* Shake the head to expel trapped water.
* Dry the ear canal. Get a clean facial tissue. Twist each corner into a tip and gently place each tip into the ear canal for 10 seconds. Repeat with the other ear using a new tissue.
* Use an over-the-counter product, such as Swim-Ear. Drop it into the ears to fight infection. Follow package directions.
* Do not remove earwax. This protects the ear canal.
For an Insect in the Ear
Shine a flashlight into the ear. Doing this may cause the insect to come out.
Resources
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
800.241.1044