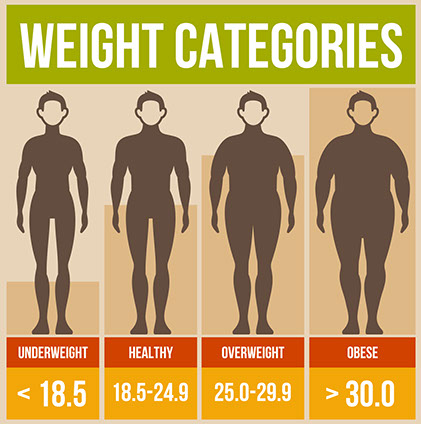
The ratio of weight-to-height is called body mass index (BMI). For adults, BMI is a common tool to classify them as normal (healthy) weight, overweight, or obese. Waist measurement, alone, is another tool.
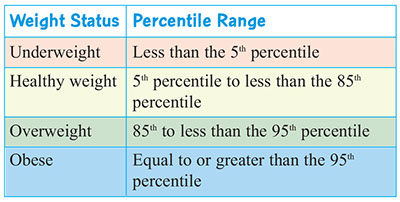
For children and teens, a BMI-for-age and how this compares to other boys or girls their same age is needed. Why? Boys and girls have different amounts of body fat and the amount and location of body fat children have change with age. A child’s BMI-for-age is plotted on a growth chart to give a percentile. This percentile defines a child’s weight status.
You can find out your child’s BMI-for-age growth chart percentile from his or her doctor and fromwww.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/bmi/index.htm.
Causes
Lack of Physical Activity
* Children spend less time playing outdoors and more time on indoor sedentary activities. On average, children spend more than four hours a day watching TV, playing video games, using a computer, and viewing DVDs. Almost three of these four hours is spent in front of the TV.
* The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that children watch no more than 2 hours of TV a day and that children younger than 2 years old watch no TV.
* Every additional hour of weekend TV watching by 5 year olds over the recommended 2 hours a day may lead to a 7% increase in risk of obesity at age 30. This means 3 hours a day can cause 7% increased risk; 4 hours a day can cause a 14% risk; 5 hours a 21% increased risk, and so on.
* Fewer than 15% of kids walk or bicycle to school compared to forty years ago when 50% did. About 60% are driven to school by a parent or other adult or teenager. One fourth of kids take the bus.
* Children get less physical activity at school. Gym classes and recess time have been cut to allow more time for an expanded curriculum.
* Places where children and teens live may be unsafe to walk and play in.
* Communities kids live in may not have places to go for recreation.
Poor Eating Habits
* Skipping breakfast. Children who usually skip breakfast are more likely to be overweight than children who usually eat breakfast. Also, children who eat breakfast have a better attention span to do schoolwork and are less irritable.
* Drinking too many soft drinks. These give empty calories. When soft drinks replace milk, children do not get the calcium and vitamin D they need for healthy teeth and bones.
* Eating meals outside the home, especially eating fast food often. In general, items chosen at fast food restaurants have a lot of calories, fat, sugar, and salt. Fruit and vegetable choices are limited, too.
* Eating meals and snacks while watching TV. Also, ads on TV promote eating fast foods, cereals with added sugar, and high calorie snacks.
* Eating too few fruits and vegetables, which have many nutrients that are needed for good health.
With poor eating habits and a lack of physical activity, children and teens take in more calories than they use up.
Genetics Factors
* Children whose parents or brothers or sisters are overweight may be at a higher risk of becoming overweight.
* Genes can affect how the body stores fat or burns calories for energy.
* Children from certain ethnic groups have higher risks for overweight and obesity. These include American Natives, African Americans, and Hispanic Americans.
Lack of Sleep
* Not getting enough sleep alters levels of hormones that regulate hunger. This leads to an increase in appetite. Studies have shown that sleep deprived people prefer foods that are high in fat, sugar, and calories.
* Not getting enough sleep can make kids drowsier during the day causing them to be less active.
* Being awake for more hours gives more time to eat.
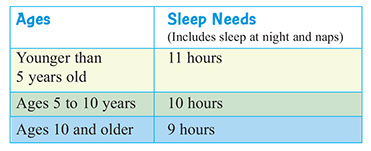
How Much Sleep Should Your Child Get?
Prevent & Control Obesity
Reasons to Prevent & Control Childhood Obesity
Children who are overweight or obese are at risk for these problems:
* Being teased and bullied.
* Low self-esteem.
* Depression.
* Asthma.
* High total blood cholesterol level and high blood pressure, which increase the risk for heart disease.
* Bone and joint problems.
* Sleep apnea. With this, breathing stops for 10 or more seconds at a time during sleep. Persons who are overweight are more prone to this because extra body tissue in the throat narrows or blocks the airway during sleep.
* Type 2 diabetes.
* Becoming overweight or obese adults.
Childhood Obesity & Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes used to be called “adult-onset diabetes” because it usually affected adults over the age of 40 who were overweight. This is no longer the case. Since the 1990s, an alarming increase in type 2 diabetes has occurred in children and teens with these risk factors:
* Being overweight.
* Not getting enough physical activity.
* Having a dad, mom, or other close relative who has diabetes.
* Being an American Indian, African American, Hispanic/Latino, Asian American, a Pacific Islander, or an Alaskan Native.
{Note: Just eating too much sugar does not cause diabetes.}
Healthy Eating
Healthy Eating at Home
* Be a good role model. Learn and follow healthy eating guidelines yourself.
* Offer healthy options for meals and snacks. This starts with buying healthy foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole-grain breads and cereals, and low-fat milk products.
* Involve your child in planning meals and shopping for healthy foods. If necessary, use checkout lanes that do not have candy and other high calorie foods on display.
* Read the Nutrition Facts label to choose foods that are lower in fat, sugar, and calories. Limit foods that are high in fats and sugars (this includes corn syrup) that provide few nutrients. Especially limit soft drinks, which give empty calories from sugar. Limit sport drinks and other fruit drinks, including juices.
* Eat meals together as a family. Do this at the kitchen or dining room table, not in front of the TV.
* Keep mealtime pleasant, not stressful.
Jump Start Your Child’s Day With a Healthy Breakfast
Here are examples:
* 1 or more servings of whole grains:
– ½ cup oatmeal.
– 1 cup dry cereal.
– 1 slice wheat toast.
– ½ whole-wheat pita pocket.
* 1 serving of milk. {Note: Children younger than 2 years should have whole milk.}
– 1 cup of low-fat or nonfat milk.
– 1 cup of low-fat or nonfat yogurt.
– 1 ounce of low-fat cheese.
* 1 serving of fruit:
– Whole or sliced orange, banana, or apple.
– 2 tablespoons raisins.
* 1 serving of meat or beans:
– 1 hard cooked egg.
– ½ ounce of almonds or walnuts.
– 1 to 2 tablespoons of peanut butter.
– 2 tablespoons of hummus.
* Do not use food as a way to punish or reward. Rewarding children with sweet treats teaches them to eat sweets in the future when they are upset, etc.
* Eat fast food less often. When you do pick up fast food, choose healthier options, such as milk instead of soft drinks; fruit cups instead of French fries; and smaller sandwiches instead of larger ones. And, add one or more servings of vegetables and fruits to fast food meals.
* Keep healthy snack foods on hand. Wash fresh fruit and put it in a bowl on the kitchen counter or table to make it easy for your child to eat.
Healthy Snacks
* Apples, oranges, bananas, strawberries, and other fresh fruits.
* Canned peaches, pears, and other fruits canned in light syrup or juice.
* Raisins and other dried fruits (in small amounts).
* Fresh vegetables, such as carrot sticks, celery sticks, and cucumber slices.
* Whole-wheat pita bread with hummus (chick pea spread), lettuce and tomato.
* Animal crackers, graham crackers, and whole-wheat crackers. Look for ones that say no trans fats on the label.
* Peanut butter on rice cakes, whole-wheat crackers, or celery.
* Low-fat yogurt with whole-grain cereal sprinkled on top.
* Whole-grain cereals, such as Cheerios, Wheaties, and bran cereals. Look for ones that have 2 or more grams of dietary fiber per serving.
* Low-fat frozen yogurt.
* Frozen fruit bars.
* Pretzels.
For children age 4 years old and younger, give foods that are soft and cut up in small pieces to help prevent them from getting something caught in their throats. Children age 4 years old and younger can easily choke on foods that are small and round, hard to chew, or are sticky. Examples are:
* Peanuts and other nuts.
* Popcorn.
* Hot dogs (even when cut in small pieces).
* Raisins and other dried fruits.
* Raw carrots.
* Chewing gum.
* Peanut butter from a spoon.
* Hard candy, sunflower or pumpkin seeds. (Wait until a child is 5 years old to give these.)
* Supervise your child when he or she eats.
Healthy Eating at School
* The lunch meal at school should provide about one-third of your child’s daily vitamin, mineral, and calorie needs. These needs can be met through foods offered at school and/or from food items brought from home.
* If your child’s school has a lunch program, find out what the menu options are. Even in a school cafeteria, menu choices can be too high in fat and calories. Promote fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are rich sources of vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. Talk to your child about the foods and beverages the cafeteria and vending machines offer. Ask which ones he or she chooses.
Encourage your child to choose:
* Low-fat and nonfat milk and water instead of soft drinks.
* Soups.
* Fruits and vegetables.
* Whole-grain breads and rolls instead of doughnuts and pastries.
* Baked instead of fried foods.
Send Milk Money & Lunch Items from Home with Your Child.
Examples are:
* Peanut butter and jelly or lean luncheon meats on whole wheat bread.
* Raw carrots, celery, cucumber, and other raw vegetables.
* Fresh or canned fruits.
* Puddings made with low-fat milk.
* Low-fat yogurt.
* Dinner leftovers, such as a baked chicken leg, salad greens with a small amount of salad dressing, dinner roll, etc.
* Soup, especially on cold days.
If you send a lunch with your child, keep cold foods cold with a small ice pack or ice in a bag. Keep hot foods hot in an insulated jar or bottle. Let your child choose an insulated lunch bag that he or she likes to carry these lunch items in.
Be More Active
Ways to Be More Active
* Children should get a total of 60 or more minutes of physical activity a day. Children who are not used to being active should start with as many minutes as they can handle and build up to at least 60 minutes a day.
* Be a good role model. Be active yourself.
* Set time limits for computer use, DVD and TV time. Do not allow your child to have a TV in his or her bedroom. When your child does watch TV, encourage him or her to get up and move, at least during commercials. These add up to eight to 19 minutes per half-hour TV show! Keep a jump rope by the TV so your child can use it during commercials and even during the program.
* Encourage your child to take part in a team sport, such as bowling or soccer, or to join an activity through school or the local community. If your overweight child is not comfortable in group activities, encourage ones that he or she likes to do and that do not embarrass your child.
* Do activities as a family. Do ones that are fun for your child and ones that he or she wants to do.
* Assign active chores for your child, such as walking the dog, vacuuming, etc.
Childhood Obesity is on the Rise
More children and adolescents in the U.S. are overweight or obese than ever before.
* The American Obesity Association says that three times as many kids in the U.S are obese as compared to 1970.
* National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) have been taken over a 30 year time span. Results from 1971−1974 to 2003−2004 (the most recent published data), show an increase in the percent of children and teens who are overweight.