First Aid
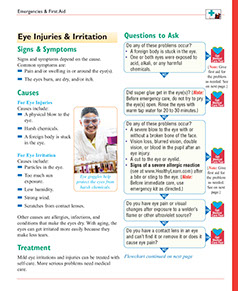
Signs & Symptoms
Signs and symptoms depend on the cause. Common symptoms are:
* Pain and/or swelling in or around the eye(s).
* The eyes burn, are dry, and/or itch.
Causes
For Eye Injuries
* A physical blow to the eye.
* Harsh chemicals.
* A foreign body is stuck in the eye.
For Eye Irritation
* Particles in the eye.
* Too much sun exposure.
* Low humidity.
* Strong wind.
* Scratches from contact lenses.
Other causes are allergies, infections, and conditions that make the eyes dry. With aging, the eyes can get irritated more easily because they make less tears.
Treatment
Mild eye irritations and injuries can be treated with self-care. More serious problems need medical care.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
For a Foreign Body Sticking Into the Eye
* Do not remove the object.
* Don’t press on, touch, or rub the eye.
* Cover the injured eye with a clean object, such as a paper cup that will shield, but not touch the eye or the foreign object. Use tape to hold the cup in place without putting pressure on the eye or the foreign object.
* Gently cover the uninjured eye with a clean bandage and tape, too. This helps to keep the injured eye still. Get Immediate Care!
For Harmful Chemicals in the Eye(s)
* Flush the eye(s) with water immediately!
* Hold the injured eye open with your thumb and forefinger. At the faucet or with a pitcher or other clean container, flush the eye with a lot of water. Start at the inside corner and pour downward to the outside corner. This lets the water drain away from the body and keeps it from getting in the other eye.
* Keep pouring the water for 10 to 30 or more minutes. Flush the eye with water until you get medical help.
* If both eyes are injured, pour water over both eyes at the same time. Or, flush one eye at a time with water. Switch back and forth quickly to treat both eyes. Or, place the face in a sink or container filled with water. Tell the person to move his or her eyelids up and down and remove the face from the water to take breaths. Use this method if chemicals get in your eyes and you are alone.
* Loosely bandage the eye with sterile cloth and tape. Don’t touch the eye. Get Medical Care Right Away!
For a Bruise from a Minor Injury that Surrounds the Eye, But Does Not Damage the Eye Itself
* Put a cold compress over the injured area right away. Do this for 15 minutes, every hour, for 48 hours.
* Take an over-the-counter medicine for the pain and swelling.
* After 48 hours, put a warm compress over the injured area.
* Seek medical care if these measures do not help.
To Remove a Foreign Particle On the White of the Eye or Inside the Eyelids
* Do not remove an object stuck in the eye, a metal chip, or a foreign body over the colored part of the eye.
* Wash your hands.
* If the foreign object is under the upper lid, look down and pull the upper lid away from the eyeball by gently grabbing the eyelashes. Press a cotton-tipped swab down on the skin surface of the upper eyelid and pull it up and toward the brow. The upper lid will invert.
* Twist a piece of tissue. Moisten the tip with tap water (not saliva). Gently try to touch the speck with the tip. Carefully pass the tissue over the speck which should cling to the tip.
* Do not rub the eye or use tweezers or anything sharp to remove a foreign object.
* Gently wash the eye with cool water.
For Dry, Irritated Eyes
With your doctor’s okay, use over-the-counter artificial tear drops, such as Ocu-Lube. Refrigerate the solution, if needed. Wash your hands before using.
For an Insect Bite Without a Severe Allergic Reaction
* Wash the eye(s) with warm water.
* Take an antihistamine if okay with your doctor.
Prevention
* Wear safety glasses when your eyes are exposed to sawdust, etc. Wear sunglasses that block UV rays.
* When using harsh chemicals, wear rubber gloves and protective glasses. Don’t rub your eyes if you’ve touched harsh chemicals. Turn your head away from chemical vapors.
* To help prevent dry eyes, use a humidifier. Limit exposure to smoke, dust, and wind. Don’t drink alcohol.
* Use artificial tear drops with your doctor’s okay.
* Don’t stare directly at the sun, especially during a solar eclipse.
* Don’t use eye makeup when an allergy or chemical irritant bothers your eye(s).
* Don’t allow a child to stick his or her head out of the window of a moving car, etc. Sand, insects, and other flying objects can strike the eye and irritate or damage the cornea.
* Don’t let children play with or near sparklers, bottle rockets, and other fireworks.