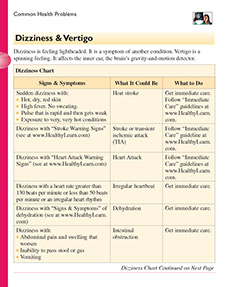
Dizziness is feeling lightheaded. It is a symptom of another condition. Vertigo is a spinning feeling. It affects the inner ear, the brain’s gravity-and-motion detector.
Dizziness Conditions
Heat Stroke
Signs & Symptoms
Sudden dizziness with:
* Hot, dry, red skin
* High fever. No sweating.
* Pulse that is rapid and then gets weak
* Exposure to very, very hot conditions
What to Do
Get immediate care.
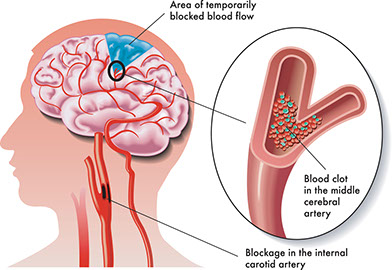
Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with “Stroke Warning Signs“
What to Do
Follow “Immediate Care” guideline.
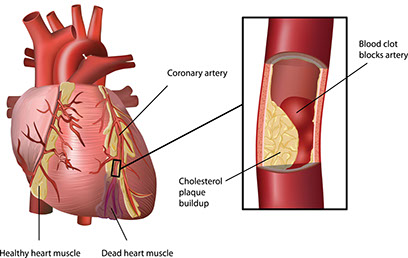
Heart Attack
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with “Heart Attack Warning Signs“
What to Do
Follow “Immediate Care” guidelines
Irregular Heartbeat
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with a heart rate greater than 130 beats per minute or less than 50 beats per minute or an irregular heart rhythm
What to Do
Get immediate care.
Dehydration
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with “Signs & Symptoms” of dehydration
What to Do
Get immediate care.
Intestinal Obstruction
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with:
* Abdominal pain and swelling that worsen
* Inability to pass stool or gas
* Vomiting
What to Do
Get immediate care.
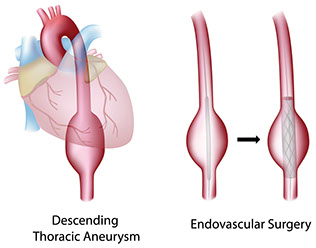
Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm
This is a tear in the main artery from the heart.
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness and fainting. Severe chest pain with extreme pain felt across the upper back (not just on one side) that came on within 15 minutes for no apparent reason, such as an injury or back strain. The pain can spread to the abdomen.
What to Do
Get immediate care. (Do not take aspirin.)
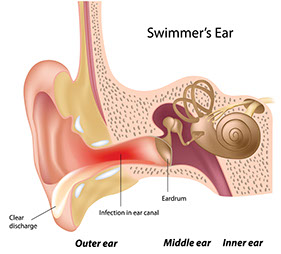
Ear Infection
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with ear pain, ringing in the ear, pus or other ear discharge, fever
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Labyrnthitis
This is an inflammation in the ear that usually results from an upper respiratory infection.
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with:
* True spinning sensation
* Loss of balance
* Nausea and vomiting
* Ringing in the ears
* Jerky movements of the eye
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Low Blood Sugar
This can occur in persons taking insulin or oral pills for diabetes and/or after not eating for 4 or more hours.
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness with hunger, sweating, trembling, anxiety, and confusion
What to Do
Use self-care.
Temporary Drop in Blood Pressure (Orthostatic Hypotension)
This could be a side effect of taking medicines, such as ones for high blood pressure and depression.
Signs & Symptoms
Dizziness when getting up too quickly from a seated or lying position
What to Do
Use self-care.
Other Causes of Dizziness:
* Alcohol
* New medications, antibiotics, or high doses of aspirin
* A change in altitude or motion sickness
* Sudden movement, such as with turning the head quickly
* Seeing fast moving objects Treatment for dizziness depends on the cause.
Vertigo
Signs & Symptoms
* Wooziness
* Sense that the room is spinning
* Nausea
* Blurred vision
* Floating, rocking, and/or rolling feeling
* Sense of walking on an uneven surface
* Loss of balance
Causes, Risk Factors & Care
Vertigo is caused by a problem with the inner ear. Causes of vertigo are:
* Benign Positional Vertigo (BPV). This is the most common type. It may happen when you turn over in bed, get up, sit down, bend over, or just tilt your head. The sensations start within seconds of changing positions and last less than a minute. As bothersome as BPV is, it rarely signals more serious disease. Risk factors for BPV are aging, viral infections, and a prior head injury.
* Ménière’s disease. This condition may be due to spasms of blood vessels in the inner ear, fluid retention in the inner ear, or allergic reactions. Ménière’s disease is linked with a decrease in hearing and tinnitus. It sometimes leads to permanent hearing loss.
* Multiple sclerosis. With this, the covering that protects nerves (myelin) is destroyed. Over time, scar tissue (sclerosis) forms where the myelin used to be in the brain and spinal cord. Scar tissue or inflammation in the brain may cause vertigo symptoms.
After proper diagnosis, most cases of vertigo are easily treated in the doctor’s office or at home with self-care.
While attacks of Ménière’s disease can continue for many years, some symptoms can be controlled with medication.
Self-Care
For Orthostatic Hypotension:
* Don’t jump out of bed. Go from a lying position to a sitting position slowly. Sit on the edge of the bed a few minutes. Stand up slowly.
* From a sitting position, stand up slowly. Hold onto the arms of the chair or the head of the bed for support.
* If you feel lightheaded, sit back down for a few minutes. Take a few deep breaths. Get up again, slowly.
For Benign Positional Vertigo (BPV):
* Sit on the side of the bed and lean to your right, resting the right ear on the bed. This might make you dizzy and nauseous at first.
* Wait 20 seconds until the dizziness stops and sit up straight.
* Wait another 20 seconds and repeat steps 1 and 2 on your left side.
* Do this exercise 10 to 15 times, 3 times a day.
For Ménière’s Disease:
* Lie still in bed until the dizziness and nausea are gone.
* Walk with assistance.
* Don’t change positions too fast.
* Do not drive, climb ladders, or work around dangerous machinery.
* Decrease the amount of salt and fluids in your diet.
* Avoid bright lights. Do not read when you have a spinning feeling.
* Resume your normal activities when symptoms go away.
* Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco.