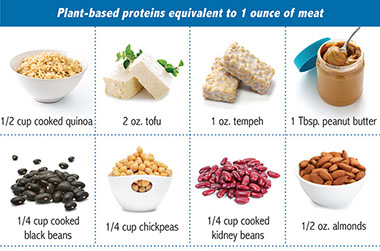
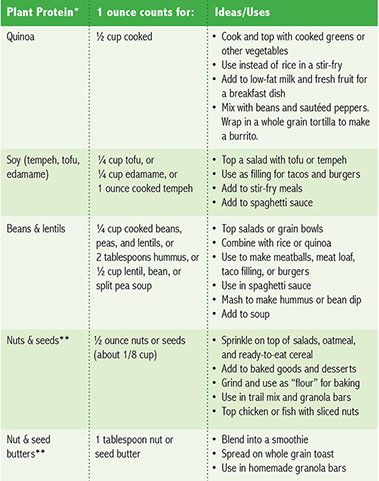
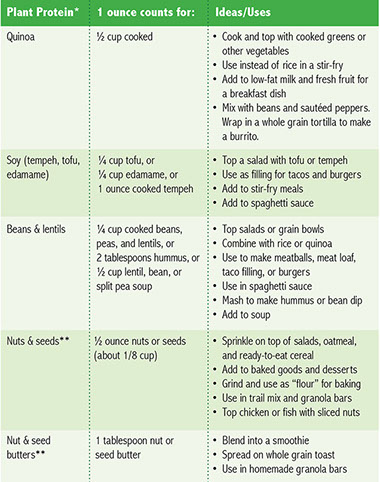
* You can get all the protein your body needs by eating a balanced and varied diet of plant foods if you choose not to eat foods that come from animal products.
** Choose unsalted or low-salt nuts and no sugar added butters to reduce sodium and added sugars.
Varieties of Seeds & Nuts
* Sunflower seeds
* Sesame seeds
* Flax seeds
* Pumpkin seeds
* Peanuts
* Cashews
* Almonds
* Walnuts
* Pecans
* Pine nuts
* Nut or seed butter
Fun Fact: Peanuts are actually a legume. For planning your meals, consider them a nut. Count peanuts and peanut butter in the protein group.
Lean Animal Protein
Use a food scale to weigh animal protein. For deli meat and processed meats (e.g., sausage), use the nutrition facts to determine how many slices or pieces equal one ounce. For thicker cuts of unprocessed meat, estimate by comparing to a deck of cards. A deck of cards is the same size as about 3 ounces of meat. Choose lean animal proteins. Poultry (chicken and turkey) is leaner than red meat (beef) or processed meats (e.g., sausage or bacon).
Leanest Cuts (Choose More of These)
* Fish
* Chicken breast
* Turkey breast
* Ground turkey or chicken breast (90% lean or higher)
* Pork tenderloin
* Venison (deer meat)
Medium Fat (Choose Fewer of These)
* Dark meat from chicken or turkey (meat from thighs or legs)
* Ground beef, 90% lean or leaner
* Ground turkey or chicken, less than 90% lean
* Beef: chuck shoulder roast, top round, tenderloin, flank steak, or round steak
Highest Fat (Limit These)
* Ground beef (less than 90% lean)
* Ribs (beef or pork)
* Beef brisket
* Sausage
* Bacon
* Bologna, pepperoni, salami
* Spam
* Hot dogs
Lean Cooking Tips for Animal Protein
* Remove the skin from chicken to reduce fat. Trim visible fats from meat before cooking.
* Use liquid fats in cooking (canola or olive oil) instead of solid fats (butter or shortening).
* Poach chicken or fish in water, stock, or white wine. When roasting or broiling, place meat on a rack in a pan so that the fat drips off the meat.
* Place fish or chicken on foil or parchment paper. Add fresh herbs, lemon juice, and tomatoes; fold up and bake. This will help seal in flavors and juices.
* Tenderize leaner cuts of meat by pounding, marinating, or cooking in a pressure cooker.
Deep frying is not a lean-cooking technique. Limit deep fried foods.
Eggs
One ounce counts as: 1 egg
Eggs are a great source of protein. Eat the whole egg (including the yolk) to get many important nutrients. These include:
* Choline, which promotes normal cell activity and liver function
* Lutein and zeaxanthin, which help maintain eye health
* B vitamins that help with energy production in the body
Eating just the egg white also provides protein. However, you will miss out on many important nutrients found in the yolk.
Ideas for Adding Eggs to Your Meals and Snacks:
Eggs can be quickly prepared on the stove or in the microwave. Add a pinch of pepper for a flavorful, on-the-go meal or snack. Eggs can be added to many dishes:
* Stir-fry
* Burritos
* Chili
* Tacos
* Burgers (as a topping or in place of meat)
* Eggs provide a filling base for vegetables. Scramble, poach, or pan-fry an egg with cooking spray. Add peppers, onions, spinach, mushrooms, tomatoes, or other colorful vegetables.
Microwave Scrambled Eggs:Add 1 tablespoon milk per egg and whisk in a microwave-safe bowl. Microwave on high for 1 minute. Stir and cook for 1 more minute (or until done).
Oaty Eggs Florentine:Coat a small pan with cooking spray and fry one egg. Add the cooked egg to cooked oatmeal and stir in spinach and cheese.
Blueberry Mug Cake:Mix 1 egg with 3 teaspoons oatmeal, 10 blueberries, and a small mashed banana in a microwave safe mug. Mix in 2-3 drops vanilla extract. Microwave on high for 3 minutes. Top with low-fat yogurt.
Fish & Seafood
Fish and seafood are lean protein sources. Add a variety of the following choices into your weekly meal plan. If you eat animal protein, include fish at least once a week*.
Types of Fish:Tuna, salmon, snapper, cod, flounder, haddock, halibut, perch, pollock, trout, tilapia
Types of Seafood:Clams, lobster, oysters, scallops, shrimp, sardines, herring
Tips for Choosing Fish:
* Fresh: Keep refrigerated until ready to cook. Prepare within a few days or freeze.
* Frozen: Thaw in the refrigerator overnight before cooking.
* Canned: Choose canned tuna or salmon packed in water. Drain before using. Canned fish usually costs less than fresh or frozen fish.
* Pouch: Choose ready-to-eat tuna that is packed in water. Get packets that don’t include mayonnaise. If needed, add a teaspoon of olive oil for moisture.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are an essential fat. This means the body needs to get that type of fat from food. Omega 3-fatty acids help:
* Keep cells healthy, including brain cells responsible for memory
* Regulate blood clotting and contraction and relaxation of arteries
* Reduce inflammation
* Regulate genetic function
Fish sources of omega-3 fatty acids:Salmon, anchovies, albacore tuna, mackerel, lake trout, halibut, sardines, oysters, and herring
Plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids:Walnuts, ground flaxseeds (and oil), canola oil, soybean oil
* If you are planning to become pregnant or have young children, you are more sensitive to higher mercury levels found in some fish. Visitwww.epa.gov/fish-tech/epa-fda-advice-about-eating-fish-and-shellfishfor more information.