Diabetes is too much sugar (glucose) in the blood. Glucose needs to get into the cells to be used for energy. Insulin is the hormone needed for glucose to get from the blood into the cells. Diabetes results when no insulin is made, not enough insulin is made, or the body does not use insulin well.
Types of Diabetes
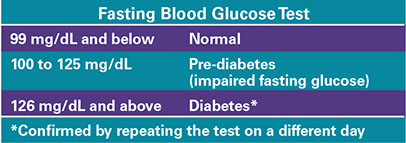
One test used to diagnose diabetes is a fasting blood glucose test.
Overweight and obese adults between ages 40 and 70 years old should be tested for adnormal blood sugar levels and type 2 diabetes. Follow your doctor’s advice for screening tests for diabetes.
Type 1
With this type, the pancreas gland makes no insulin or very small amounts. Often, the pancreas has fewer cells that make insulin. This type most often occurs in children and young adults. It can happen at any age, though.
Type 2
With this type, the pancreas does not make enough insulin or the body does not use insulin the right way. Often, this occurs in persons who are overweight and/or who don’t exercise. Modest weight loss and moderate physical activity can delay or help prevent type 2 diabetes.
Pre-diabetes
With this type, blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes. Many people with pre-diabetes develop type 2 diabetes within 10 years. Modest weight loss and moderate physical activity can delay or help prevent type 2 diabetes.
Gestational
This type occurs during pregnancy. It usually ends when the pregnancy ends. It does, though, increase the risk for the mother to get diabetes in the future. The mother will need follow-up blood sugar checks.
Signs & Symptoms
In the U.S., about 27 percent of people with diabetes do not know they have it. They may not have symptoms. According to the American Diabetes Association, some signs and symptoms of diabetes are:
* Urinating often
* Unusual thirst
* Extreme hunger
* Unusual weight loss
* Extreme fatigue
* Being very cranky
* Blurry vision
If you have any of these symptoms, see your doctor. In type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly. In type 2, symptoms tend to come on more slowly. You can even have diabetes without any symptoms.
A screening test can detect diabetes early. Early treatment may reduce other health problems related to diabetes.
Diabetes has no cure, but it can be controlled. Goals are to keep blood sugar levels between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals; and less than 180 mg/dL two hours after starting a meal.
Health Problems Related to Diabetes
When diabetes is left untreated or not treated well, you are at an increased risk for these health problems:
* Heart disease
* Stroke
* Poor circulation
* Foot problems
* Infections in general and slow healing of wounds and infections
* Yeast infections, especially in women
* Kidney and eye problems. This includes blindness.
* Gangrene. Sometimes this is so severe that the affected limb must be amputated.
Risk Factors
Discuss your risk for diabetes with your doctor or health care provider.
For Type 2 Diabetes
* Your mother, father, brother, and/or sister has or had diabetes.
* You are overweight. You are not physically active.
* You are age 45 or older.
* You are female with a past history of gestational diabetes and/or you had at least one baby who weighed more than 9 pounds.
* You come from ethnic groups that are more prone to diabetes: African Americans, Latinos, Native Americans, Asian Americans, and Pacific Islanders.
For Type 1 Diabetes
* You have a family history of type 1 diabetes.
* You had a virus that has injured the pancreas gland or a problem that has destroyed cells in the pancreas gland that make insulin.
Medical Care
Medication
Diabetes pills. These are prescribed when diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar. Types include:
* Ones that delay or block the breakdown of starches and some sugars (e.g., acarbose).
* Ones that help your body release more insulin (e.g., glyburide and tolbutamide).
* Ones that lower blood sugar without helping your body make more insulin (e.g., metformin).
Insulin. There are different types based on how fast and over how many hours they work. People with type 1 diabetes need insulin. Some persons with type 2 diabetes need insulin. It can be given through:
* Insulin injections (shots)
* Insulin pump therapy
Other medicines, as needed, to control blood pressure, blood cholesterol levels, etc.
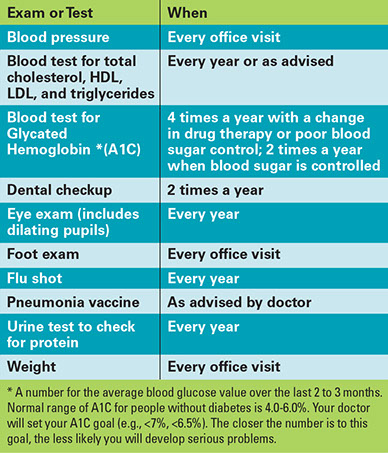
Exams & Tests
If you have diabetes, have exams and tests, as advised. In general, diabetics should have the following:
Self-Care
Keep Track of Your Blood Glucose
* Test your blood sugar, as advised. People with type 1 diabetes may be told to test before each meal and at bedtime. People with type 2 diabetes may be told to test every other day or daily and at certain times.
* Keep a log of your blood sugar results. Note any reasons that could help explain why your blood sugar is higher or lower than usual. Share this log with your health care provider.
Foot Care
* Check your feet every day. Let your health care provider know of any problems (swelling, redness, other color changes, ingrown toenails, corns, and foot injuries). Use a mirror to look at the bottom of your feet.
* Keep your feet clean.
* Wear shoes and slippers that fit your feet well. Don’t go barefoot, indoors or outdoors.
* Cut nails straight across and not too close to the skin. Have a foot doctor cut your toenails, if advised.
Skin Care
To reduce the risk of skin problems and infections:
* Keep your skin clean. Bathe or shower, daily, with warm water and a mild soap.
* Apply lotion to your skin to keep it moist.
* Protect your skin from damage.
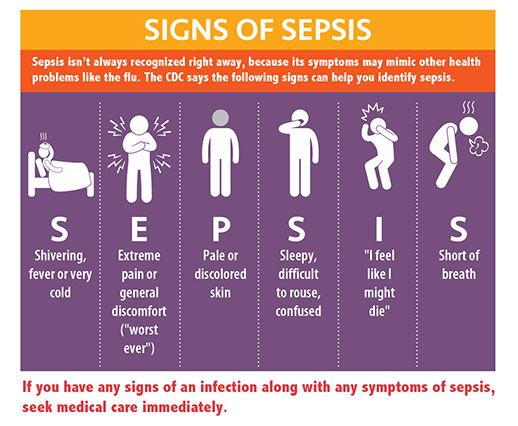
– Avoid cuts, scrapes, punctures, etc. If you get a skin injury, treat it right away. Keep it clean and cover the area with a clean, dry bandage. Call your doctor if the injury does not start to heal in a day or two or if you notice signs of infection (redness, swelling, pus, throbbing, and pain).
– Avoid sunburn. Use a “broad spectrum” sunscreen, with an SPF of 15 or higher.
– Wear gloves in cold weather and when you do work that may injure your hands.
Diet
In general, you may be advised to:
* Lose weight if you are overweight.
* Eat meals at regular times.
* Follow a meal plan for breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks. You may be told to count carbohydrates. Books, booklets, and food labels list carbohydrate amounts.
* Have 20 to 35 or more grams of dietary fiber per day. Fiber is in bran, whole-grain breads and cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables, beans and peas, and seeds.
* Strictly limit saturated and trans fats. To do this, choose nonfat dairy products; very lean meats (and in small amounts); and limit all animal and “hydrogenated fats.”
* Limit alcohol. Follow your doctor’s or health care provider’s advice.
Exercise
Regular exercise helps control your weight and blood sugar. It also lowers your blood cholesterol, blood pressure, and risk of heart disease. Exercise may also reduce the amount of medicine you need to take for your diabetes and make you feel better.
* If told to, test your blood glucose before and after exercise.
* When you exercise, have with you a carbohydrate source, such as fruit juice, hard candies, or glucose gel or tablets. For each of these, take the amount as advised by your health care provider.
* Find out if you should also carry a glucagon emergency kit. Your doctor needs to prescribe this. You and persons you exercise with should learn how to use this.
Diabetic Emergencies
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
This can happen if you: Skip or don’t finish meals or snacks or wait too long to eat; exercise more than usual; and/or take excess diabetes medicine or insulin.
Symptoms
* Shaky feeling. Weakness. Dizziness.
* Rapid pulse. Shallow breathing.
* Sweating. Cold, clammy skin.
* Sudden blurred or double vision
* Numbness or tingling around the mouth and lips
* Sudden mood changes. Confusion.
* Faintness. You may pass out.
What to Do
If you can, check your blood sugar. If it is lower than the level set by your health care provider, such as 70 mg/dL, have 15 grams of a “fast acting” carbohydrate. Examples are:
* 1/2 cup (4 ounces) fruit juice or regular (not diet) pop
* 5 or 6 regular (not sugar-free) hard candies
* 4 teaspoons of sugar or honey
* 6 to 10 gumdrops or jelly beans
* 3 glucose tablets (or the number your health care provider advises). Drug stores sell these.
* 1 cup (8 ounces) of milk
* If you don’t feel better after 15 minutes, take the same amount of sugar source again. If you still don’t feel better, call your doctor.
* If a person with diabetes passes out, can’t swallow, or can’t be roused, get emergency care. Use a prescribed emergency glucagon kit to inject glucagon. If there is no glucagon, rub sugar or any type of sweet paste, such as cake frosting, inside the person’s mouth. Call for emergency medical care. Do not give insulin, food, or liquids.
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
This can happen if you: Get sick; eat too much; don’t do your normal exercises; don’t take your insulin or your diabetes pills or don’t take enough of them.
Symptoms
* Extreme thirst
* Urinating often
* Nausea
* Acting cranky
* Dry, itchy skin
* Feeling very sleepy
* Blurred vision
What to Do
* Check your blood sugar. Follow your doctor’s advice for your blood sugar level. If it is over 240 mg/dL or if you are sick, you may be told to check your urine for ketones. Call your doctor right away if your urine shows moderate or large amounts of ketones.
* Follow your treatment plan more closely.
High Blood Sugar with Ketones in the Blood
This is a serious condition. It can result in a coma. It occurs in persons who have type 1 diabetes. It is called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Early Symptoms
* Intense thirst. Dry mouth.
* High blood glucose levels
* Urinating often
* Positive urine ketone tests
Later Symptoms
* Tiredness. Dry, flushed skin.
* Nausea and/or vomiting
* “Fruity” breath odor
* Hard time breathing. Usually short, deep breaths.
* Lethargy. Can’t be roused.
What to Do
* Call your doctor right away for advice.
* If you can’t reach your doctor, get to a hospital emergency department right away.
High Blood Glucose without Ketones
This is called hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketonic syndrome (HHNS). It occurs most often in persons who have type 2 diabetes. It usually comes after another illness, such as the flu, that caused dehydration. If it is not treated, seizures, coma, and even death can occur.
Symptoms
* Dehydration. This may be the only symptom.
Warning Signs of HHNS
These occurred days or weeks before HHNS.
* Extreme thirst
* Very high blood glucose levels (over 600 mg/dL)
* High fever
* May have vision loss
* Sleepiness or confusion
What to Do
* Drink water
* Get to a hospital emergency department right away.
Resources
American Diabetes Association
800.DIABETES (342.2383)
www.diabetes.org
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
www.niddk.nih.gov