Medical Care
It is better to prevent an illness than to get it. The next best thing is to detect and treat an illness early.
Prevention
* Maintain a healthy body weight.
* Do regular exercise.
* Eat healthy.
– Eat 5 or more servings of fruits and vegetables a day. Eat whole-grain breads, cereals, and bran. Eat kidney and other beans, peas, and soy foods, such as tofu.
– Have 20 to 35 grams of dietary fiber a day.
– Follow a low saturated fat diet. Strictly limit trans fats.
– Limit cholesterol to 300 milligrams per day.
– Eat salt-cured, salt-pickled, and smoked foods only once in a while, if at all.
* Limit alcohol to 2 drinks per day for men; 1 drink per day for women and persons age 65 and older.
* Don’t smoke or use tobacco products. Avoid secondhand smoke.
* Limit exposure to cancer causing agents, such as asbestos, pesticides, etc.
* Have X-rays only when needed.
* Limit your exposure to the sun, sun lamps, and tanning booths. When you are in the sun, protect your skin.
* Manage stress.
* Take the medicines your doctor prescribes.
* Talk to your doctor about taking vitamins, minerals, and other supplements.
* Have regular health screenings.
* Ask your doctor if there are other things you can do to lower your risk for health problems, especially if you are at a high risk for them. Examples include:
– Breast cancer
– Diabetes
– Heart disease
– High blood pressure
– Osteoporosis
– Stroke
* Adults should also be screened for alcohol misuse, depression, obesity, and tobacco use. If you are at an increased risk for an illness, tests may need to be done sooner. Extra tests, such as screenings for diabetes, may also be needed. Follow your doctor’s advice.
1. Screening guidelines vary with different health groups. For ages 40-49 and 75+, discuss your risk for breast cancer and the pros and cons of screening with your doctor. If you are at a high risk for breast cancer, seek expert medical advice about screening and prevention.
2. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test screening guidelines vary with different health groups. Ask your doctor if and at what age you should start discussing the benefits and risks of getting PSA blood tests.
Cancer
When cancer first develops, there may be no pain or other signs. That’s why screening tests are important. As different types of cancers grow, warning signs may be present. These signs may be due to problems other than cancer, too. See your doctor to find out. In many cases, the sooner cancer is found and treated, the better the chances for a full recovery.
For Bladder Cancer
* Blood in the urine. The color of the urine can be deep red or it can be a faint rust or smokey color.
* Pain when you urinate.
* The need to urinate often or urgently.
For Breast Cancer
* A lump or thickening: In the breast; in the surrounding area; along the collar bone and below the breast; or in the underarm area.
* A change in the size or shape of the breast.
* A nonmilky or bloody discharge from the nipple.
* A change in the color or feel of the skin of the breast, nipple, or areola (the brown or pink area around the nipple). Dimpled, puckered, or scaly skin.
For Colon and Rectal Cancers
* A change in bowel habits.
* Constipation. Having stools more often and/or loose stools.
* A feeling that the bowel does not empty all the way.
* Blood in or on the stool. This can be bright red or very dark in color.
* Stools that are more narrow than usual.
* Stomach bloating, fullness, and/or cramps.
* Frequent gas pains.
* Weight loss for no known reason.
* Constant tiredness.
For Kidney Cancer
* Blood in the urine.
* A lump or mass that can be felt in the kidney area.
* A dull ache or pain in the back or side.
* An unexplained cough for more than 3 weeks.
For Lung Cancer
* A cough that doesn’t go away. This could be a “smoker’s cough” that gets worse.
* Constant chest pain. Back pain in some persons.
* Hoarseness.
* Shortness of breath and wheezing.
* Recurring pneumonia or bronchitis.
* Coughing up blood.
* Fatigue, appetite loss and weight loss.
* Weakness in your shoulder, arm, or hand.
For Ovarian Cancer
Often, there are no early symptoms. When symptoms appear, they include:
* Swelling, bloated feeling, or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
* Feeling full even after a light meal. Loss of appetite and weight.
* Gas. Indigestion. Nausea.
* Diarrhea, constipation, or frequent urination.
* Bleeding from the vagina.
Often, the cancer has spread by the time it is found.
For Prostate Cancer
Early prostate cancer often does not cause symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include:
* A need to pass urine often, especially at night.
* A hard time starting to urinate, holding back urine, or not being able to pass urine.
* Weak or interrupted flow of urine.
* Pain or burning feeling when you pass urine.
* Pain when you ejaculate.
* Blood in the urine or semen.
* Frequent pain or stiffness in the lower back, hips, or upper thighs.
For Testicular Cancer
* A lump in a testicle
* A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
* A dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin
* A sudden build up of fluid in the scrotum
* Pain or discomfort in a testicle or the scrotum
* Enlarged or tender breasts
Males aged 15 and older should do a testicular self-exam (TSE) if and as often as advised by their doctors to look for any lumps or changes in the size or shape of a testicle.
For Throat Cancer
* Hoarseness or other changes in the voice
* A lump on the neck or feeling of a lump in the throat
* A cough that doesn’t go away
* A hard time swallowing. A feeling of fullness, pressure, or burning when swallowing.
* Repeated cases of indigestion and heartburn. Frequent vomiting or choking on food.
* Pain behind the breastbone or in the throat
Basal and Squamous Cell Cancers
* Basal cell. More than 90% of all skin cancers in the U.S. are this type. It grows slowly. It seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
* Squamous cell. This type of skin cancer spreads more often than the basal cell type. It is still rare for it to spread, though.
Basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, like the head, face, neck, hands, and arms. These skin cancers can occur anywhere, though.
Early Warning Signs of Basal and Squamous Cell Cancers
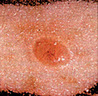
Small, smooth, shiny, pale, or waxy lump.
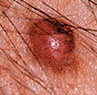
Firm red lump.
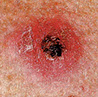
A lump that bleeds or develops a crust.
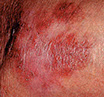
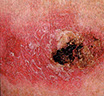
A flat, red spot that is rough, dry, or scaly.
Warning Signs of Melanoma
The first sign can be a change in an existing mole or a new or “ugly-looking” mole. The letters “ABCDE” can identify signs.
Skin Self-Exam
* Do an exam monthly, after a shower or bath. To check your skin, use:
– A well-lit room
– A full-length mirror
– A hand-held mirror
* Locate your birthmarks, moles, and blemishes. Check for a change in the size, texture, or color of a mole. Check for a sore that does not heal.
Check all areas.
1. Look at the front and back of your body in the mirror. Raise your arms and look at your left and right sides.
2. Bend your elbows and look carefully at the palms of your hands. Look at both sides of your forearms and upper arms.
3. Look at the back and front of your legs. Look between the buttocks and around the genital area.
4. Sit and closely examine your feet. Look at the soles and between the toes.
5. Look at your face, neck, and scalp. Use a comb to move your hair so you can see your scalp.
See your doctor if you find anything unusual.
Diabetes
One in three people who have diabetes do not know they have it. See your doctor if you have one or more of the signs listed below.
Signs of Diabetes:
* Frequent urination
* Excessive thirst
* Extreme hunger
* Unusual weight loss
* Increased fatigue
* Irritability
* Blurry vision
In type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly. With this type, the body either makes no insulin or only very small amounts.
In type 2 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on more slowly. The body does not make enough insulin or can’t use it the right way. This type most often occurs in persons who are over age 40, are overweight, and who don’t exercise.
Pre-diabetes occurs before type 2 diabetes. Getting diagnosed and treated for this can keep you from getting type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes can be present without symptoms. Follow your doctor’s advice to screen for diabetes. Early detection and treatment lower the chances of diabetes complications.
Heart Attack
Heart Attack Warning Signs
If heart attack warning signs occur, call 9-1-1 or your local rescue squad right away!
See your doctor if you have one or more of these signs and symptoms:
* Chest discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back. The discomfort feels like pressure, fullness, squeezing or pain.
* Discomfort in other areas of the upper body. This can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms or in the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
* Shortness of breath. Often, this comes with chest discomfort. But it can also come before the chest discomfort.
* Other symptoms. These can include breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea, or being lightheaded.
The most common heart attack symptom for both men and women is chest pain or discomfort. But women are more likely than men to have some of the other common signs, especially shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, and back or jaw pain.
Lupus
Lupus is an immune system disorder. It can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, and nervous system.
Warning signs of lupus:
* Joints ache and swell for more than 3 months.
* Fingers get pale, numb, or ache in the cold temperatures.
* Mouth sores last for more than 2 weeks.
* Blood tests show: Anemia; low white cell count, or low platelet count; and/or protein in the urine.
* A rash occurs across the nose and cheeks. It lasts for more than 1 month.
* Skin rash (not sunburn) occurs after being in the sun.
* Pain lasts for more than 2 days when taking deep breaths.
* A seizure or convulsion occurs.
Let your doctor know if you have or have had any of these warning signs. Having 3 or more of these signs may suggest lupus.
Stroke
Stroke Warning Signs
* Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
* Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding
* Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
* Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
* Sudden severe headache with no known cause
If stroke warning signs occur, call 9-1-1 or your local rescue squad right away!