Heart disease is a common term for coronary artery disease (CAD). It is the number one cause of death in the U.S. in both men and women. With heart disease, arteries that supply blood to the heart become hardened and narrowed. Heart disease can lead to these problems:
* Angina. With this, the heart muscle does not get as much blood and oxygen as it needs for a given level of work. A heart attack damages the heart muscle. Angina does not. It is a warning sign that a heart attack could occur, though.
* Heart attack.
* Heart failure (HF). With this, the heart “fails” to supply the body with enough blood and oxygen for its needs. This develops slowly. It becomes chronic.
Signs & Symptoms
* Symptoms of angina are pain, discomfort, or a squeezing pressure in the chest. Aching in a tooth, jaw, or neck can also occur. Symptoms usually go away with rest and/or nitroglycerin. Angina attacks may occur with anger, excitement, or exertion, such as walking up a hill.
* Symptoms of a heart attack.
* Symptoms of heart failure are: Shortness of breath; feeling very tired or weak; swelling in the lower legs, ankles, and feet; dry cough or one with pink, frothy mucus; rapid weight gain; and a fast heart beat.
Causes
Heart disease is caused by atherosclerosis. This is the buildup of plaque in the inner walls of the arteries. The plaque is made up of blood platelets, cholesterol, fibrous tissue, and sometimes calcium. The plaque narrows the arteries. This slows or blocks the flow of blood to the heart.
Some factors increase the risk of heart disease. The more risk factors; the higher the risk.
Risk Factors That Can’t Be Changed
* A past heart attack or stroke.
* Being a male 45 years or older.
* Being a female 55 years or older.
* Family history of heart disease:
– A father or brother had heart disease before age 55.
– A mother or sister had heart disease before age 65.
Risk Factors That Can Be Controlled
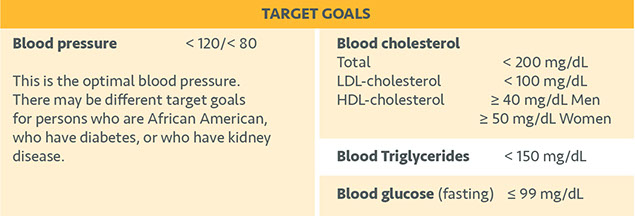
* High blood pressure.
* High-risk blood cholesterol levels.
* Smoking.
* Being overweight or obese.
* Lack of physical activity.
* Having diabetes and high total and/or LDL (bad) cholesterol.
* Using cocaine or amphetamines.
* Metabolic syndrome.
Other Factors that May Play a Role in Heart Disease
* Waist measurement > 40 inches for men; > 35 inches for women.
* C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. Levels of CRP rise when there is inflammation in the body.
* Elevated blood homocysteine levels.
* Infections, such as chlamydia pneumoniae.
* Elevated blood lipoprotein (a).
* Elevated blood triglycerides.
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms, control or reduce risk factors, stop or slow further damage to the arteries, and prevent and treat cardiac events. Treatment includes:
* Self-Care / Prevention measures on this page.
* Medications.
* Procedures to open blocked or narrowed arteries or bypass them.
* Cardiac rehabilitation (rehab).
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
* Have regular medical checkups. Get your blood pressure checked at each office visit or or as advised by your doctor. Get your blood cholesterol tested regularly, as advised by your doctor.
* Don’t smoke. If you smoke, quit.
* Get to or stay at a healthy weight.
* Take all medications as prescribed.
* If you are 50 to 69 years old, ask your doctor about the benefits and harms of aspirin therapy (e.g., 1 low-dose aspirin daily) to help prevent cardiovascular disease.
* See your doctor if you have any of the Signs & Symptoms of Diabetes.
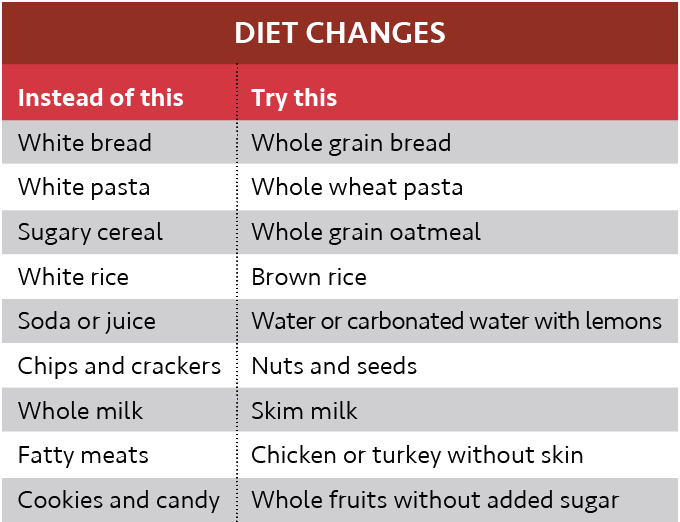
* Follow a diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Limit sodium to 1,500 to 2,400 milligrams per day. Follow theDASH Eating Plan.
* Get regular exercise. Follow your doctor’s advice.
* Manage stress. Practice relaxation techniques.
* If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Too much alcohol can raise the risk for high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. Moderate drinking, may be linked to a lower risk of coronary heart disease in some persons. Moderation means no more than 2 drinks a day for men; 1 drink a day for women and persons age 65 and older. One drink = 5 oz. of wine; 12 oz. of beer; or 1-1/2 oz. of 80-proof liquor.
* Ask your doctor how much, if any, alcohol you should drink.
* Get your doctor’s advice about taking vitamins, minerals, and herbal products.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic Syndrome is having at least three of these five conditions:
1. Abdominal obesity. Waist measurement for this varies according to sex and ethnic group. Ask your doctor.
2. High triglycerides:* ≥ 150 mg/dL
3. Low HDL-cholesterol:* < 40 mg/dL for males; < 50 mg/dL for females
4. High blood pressure:* ≤ 140 mm Hg systolic and/or ≤ 90 mm Hg diastolic
5. High fasting glucose:* ≥ 100 mg/dL
* Or taking medication to treat this condition.
Resources
The American Heart Association
800.AHA.USA1 (242.8721)
www.heart.org/HEARTORG
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
www.nhlbi.nih.gov