Conventional CPR ─ Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths {Note: Doing Hands-Only CPR is advised for persons not trained in CPR. Take a training course in CPR to learn how to do it the right way. Find out about training course in CPR to learn how to do it the right way. Find out about training atwww.cpr.heart.org.} Do CPR when the person is not responsive, is not breathing, and does not have a pulse.
Hands Only CPR
This is giving chest compressions with no rescue breaths. It can be used for adults and teens who suddenly collapse.
Hands-Only CPR is not for:
* All infants and children.
* Adults and teens who have collapsed due to near-drowning, a drug overdose, or breathing problems.
* Adults and teens who are already unconscious and not breathing normally when found.
Hands-Only CPR – 2 Steps:
1. Call 9-1-1 or get someone else to call!
2. Push hard and push fast in the center of the chest. Give 100 compressions per minute, such as to the tune of “Staying Alive” by the Bee Gees. Keep this up until an automated external defibrillator (AED) is used or EMS arrives.
See the Hands-Only™ CPR video atwww.cpr.heart.org.
CPR for Adults & Teens
Shout for help! Call or have someone else call 9-1-1 and get an automated external defibrillator (AED) if one is nearby. If another person is around, one of you stay with the person. The other one call 9-1-1 and get the AED. Follow the 9-1-1 dispatcher’s advice. Do CPR until the AED is used or EMS takes over.
1. Begin Chest Compressions:
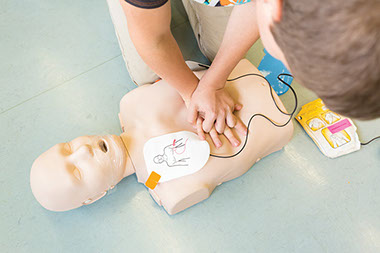
* Kneel at the person’s side. Place the heel of one hand ½ inch above where the ribs join the breastbone. Place your other hand on top of this one. Using the heels of your hands, depress the middle of the chest between the nipples at least 2 inches, but not more than 2.4 inches deep. Keep your arms straight. See image A.
* Push hard and push fast! Give at least 100 chest compressions in one minute. Relax pressure completely after each compression.
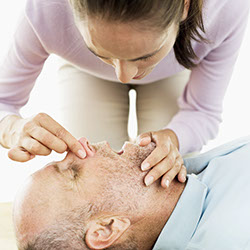
2. Open the person’s airway.
With one hand, tilt the person’s head back. With 2 fingers of your other hand, lift the chin up. See image B. If the airway is blocked, tilt the person’s head gently and slowly until the airway is open.
3. If the person is breathing, keep the airway open.
Look for other problems.
4. If the person is not breathing, take a normal, (not deep) breath, and give him or her “Rescue Breaths.”
* Pinch the nose shut. Forming a tight seal, place your mouth over the person’s open mouth. See image C.
* Give 1 full breath for 1 second. If the chest doesn’t rise, repeat head tilt chin lift. See image B. Give the 2nd full breath for 1 second. Look to see if the person’s chest rises.
5. Give cycles of 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths, without a break, until the person starts to move, an AED is used, or EMS provides care.
Children Ages 1 to Puberty
Shout for help! If you are alone, do CPR for 2 minutes before you call 9-1-1. If the child does not appear to have a serious injury, carry the child to nearest phone and call 9-1-1! Put the phone on speaker mode. Follow the dispatcher’s advice. If you are not alone, someone start CPR; someone else call 9-1-1 and get an AED, if one is nearby.
1. Place the child on his or her back.
2. Start Chest Compressions:
* Put one hand on the child’s breastbone right between his or her nipples.
* Using the heel of your hand (or both hands like in image A under Adults & Children Who Reached Puberty) push straight down about 2 inches (at least one-third of the depth of the child’s chest). See image D. Let the chest rise back up after each push.
* Push hard and push fast! Give at least 100 chest compressions in one minute. Relax pressure completely after each compression.
3. Follow steps 2, 3, 4, and 5 under CPR For Adults and Children who Have Reached Puberty on this page.
{Note: Chest compressions alone are better than doing nothing, but it is best to give chest compressions plus rescue breaths. Why? Airway problems are the main cause of cardiac arrest in infants and children.}
Babies Up to 1 Year Old
1. If you are alone, do CPR for 2 minutes before you call 9-1-1.
If the child does not appear to have a serious injury, carry the child to nearest cell or other phone and call 9-1-1! Put the phone on speaker mode. Follow the dispatcher’s advice. If you are not alone, someone start CPR; someone else call 9-1-1!
2. Start Chest Compressions:
* Put the tips of your middle and ring fingers on the baby’s breastbone right between his or her nipples. See image E.
* Slip your other hand underneath the baby’s back for support.
* Push straight down about 1½ inches (at least one-third of the depth of the baby’s chest). Push at a rate of at least 100 compressions per minute. Let the chest rise back up after each push.
3. If the baby is not breathing, or you are not sure he or she is breathing, give Rescue Breaths:
* Cover the infant’s mouth and nose with your mouth, forming a tight seal.
* Give 1 full breath for 1 second. Look to see if the chest rises. Give the 2nd full breath for 1 second and look to see if the chest rises.
* If the chest does not rise, go back to giving chest compressions. See step 2 listed above. After 30 more compressions, try rescue breaths again. {Note: If you can’t give rescue breaths, just keep giving chest compressions.}
4. Give cycles of 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths, without a break.
Do this until the baby starts to move or until EMS provides care.