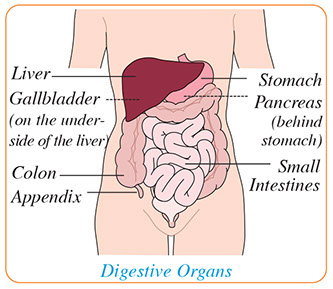
Pain in the legs or ankles can range from mild to severe. The type and amount of pain depends on the cause.
For Pain, in General
* Take an over-the-counter medicine for pain as directed on the label. If the pain is not better after a few doses, call your doctor.
* Use a heating pad (set on low), a hot pack, or a moist, warm towel on the area of pain. If the pain is due to an injury, don’t use heat for 48 hours. Use R.I.C.E.
To Help Prevent Leg Pain & Ankle Pain
* Get to and stay at a healthy weight.
* Get regular exercise. This helps to keep ankle and leg muscles strong.
* Before you exercise, stretch and warm up your muscles. When you are done, cool them down.
* Protect your knees. Use knee pads when you garden or kneel. Always land on bent knees when jumping. Avoid deep knee bend exercises.
* Don’t wear high-heeled shoes. Keep your shoes in proper shape.
* Take good care of your feet.
R.I.C.E.
* Rest the injured area for 24 to 48 hours.
* Ice the area as soon as possible. Keep doing this for 10 minutes every 2 hours for the first 48 hours. Use an ice pack, ice in a heavy plastic bag with a little water, a bag of frozen vegetables, etc. Put a thin towel between the ice pack and the skin.
* Compress the area. Wrap with an elastic bandage. Do not cut off circulation. Remove the bandage every 3 to 4 hours, for 15 to 20 minutes each time.
* Elevate the area above heart level, if possible. Place it on a pillow, folded blanket, stack of newspapers, etc.
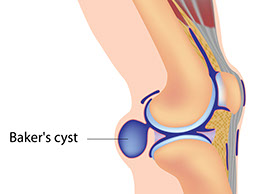
Baker’s Cyst
Signs & Symptoms
Painless or painful swelling behind the knee. May feel like a water-filled balloon.
What to Do
Call doctor.
Broken Bone or Dislocation
Signs & Symptoms
Any of the signs that follow occur after a leg or ankle injury. A bone sticks out or bones in the injured limb make a grating sound. The injured limb looks deformed, crooked, or the wrong shape. You lose feeling in the injured limb. The skin under the affected injured area is cold and blue. The limb is very painful and/or swollen or you can’t bear weight on the limb or move it.
Bursitis
Signs & Symptoms
Pain and swelling around a knee or hip joint. The pain gets worse with movement. Fever (maybe).
What to Do
See doctor.
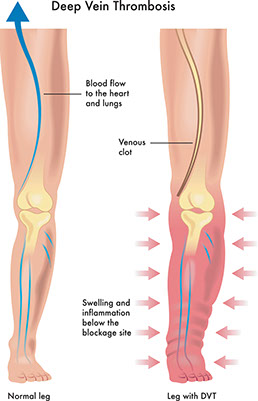
Deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) with or without a blood clot to the lung
Signs & Symptoms
Pain, redness (may have shades of red, purple, and blue), or swelling in one ankle or leg. May be followed by severe shortness of breath that came on all of a sudden. May include coughing up blood or pink-frothy sputum. Chest pain.
What to Do
Get medical care fast!
Flu
Signs & Symptoms
Aches in leg muscles and joints with fever and/or chills. Headache. Dry cough. Sore throat. Fatigue.
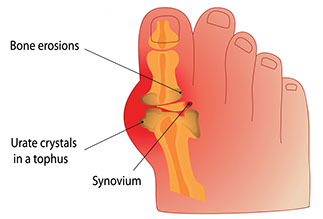
Gout
Signs & Symptoms
Sudden, severe pain in a toe, knee, or ankle joint. The pain can be felt even when clothing is rubbed against the joint. The joint area is swollen, red, or purplish in color. It also feels warm, and is very tender to the touch.
What to Do
See doctor.
Heart Failure
Signs & Symptoms
Swelling of both ankles at the same time. Shortness of breath. May have a dry cough or a cough with pink, frothy mucus.
What to Do
Get medical care fast!
Infection. Could also be Cellulitis.
Signs & Symptoms
Pain with fever, redness, tenderness, warmth and pus at a wound site. A red streak up the leg (rarely).
What to Do
See doctor.
Leg Cramp
Signs & Symptoms
Sudden, sharp, tightening pain in the leg, often the calf. The muscle feels hard to the touch. The pain subsides after a minute or so and the muscle relaxes.
Self-Care
* Walk on the leg.
* Shake the leg and then elevate it.
* Sit with your leg flat on the floor. Flex your foot upward, then toward your knee. Reach for your toes and pull them toward your knee. This stretches the calf muscles.
* Have someone massage the cramped muscle gently, but firmly.
* Apply a heating pad (set on low), a hot pack, or moist, warm towel to the muscle cramp.
* Rub the muscle that is cramping. Rub upward from the ankle toward the heart.
(Note: Do not rub a leg if you suspect phlebitis or thrombosis.)
To Prevent Leg Cramps
* Get good sources of calcium, potassium, and magnesium. See lists at left. Take calcium, potassium, and magnesium as advised by your doctor.
* Drink plenty of water and other fluids. Limit drinks with caffeine. Avoid drinks with alcohol. Doing these things can help prevent dehydration which could cause leg cramps.
* Warm up your muscles before you exercise. Cool down your muscles when you are done.
* With your doctor’s okay, wear elastic stockings while you are awake.
* Another way to stretch your calf muscles is to ride a stationary bicycle for a few minutes.
* Take a warm bath before bedtime.
* Sleep with loose-fitting blankets and night clothes. Keep your legs warm.
* If you have severe leg cramps or get them often, tell your doctor. Ask if any medication you take could cause your leg cramps. Ask for ways to treat your leg cramps.
* Before you go to bed, stretch your calf muscles. Here’s one way to do this:
– Stand an arm’s length away from a wall. Lean against it with the palms of your hands.
– Bend your left knee. Keep your right leg straight behind you. Keep both feet flat on the floor and your back straight.
– Lean forward. Feel your right calf muscle stretch. Hold the stretch as you count to 10 slowly.
– Repeat, switching leg positions.
Lyme Disease
Signs & Symptoms
Muscle or joint pain and chronic swelling of the knee joints. These problems develop months or years after a deer-tick bite and a bulls-eye red rash with pale centers.
What to Do
See doctor.
Osteoarthritis
Signs & Symptoms
Pain, stiffness, and sometimes swelling of the knee or ankle joints. Often, the joint has gotten tender over months or years and may look enlarged or deformed.
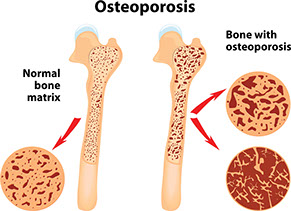
Osteoporosis
Signs & Symptoms
Leg or ankle pain with gradual loss of height; stooped posture; backache; and/or past bone fractures, especially in the wrists and hips.
Paget’s Disease
This is a bone disorder that progresses slowly. Most persons with this disease do not develop symptoms.
Signs & Symptoms
Leg pain that radiates from the lower back. Pain or stiffness in the knees. Bowing of the legs or other bone deformity. Unexplained bone fractures. May have headache, dizziness, hearing loss, and/or ringing in the ears.
What to Do
See doctor.
Self-Care / Prevention
* If needed, take an over-the-counter medicine for pain as directed on the label.
* Take other medicines as prescribed by your doctor.
* Get regular checkups to detect hearing loss.
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Signs & Symptoms
Sudden and severe pain in a leg that is not relieved with rest.
What to Do
Get medical care fast!
Signs & Symptoms
Muscle pain in one or both legs. Fatigue in the thighs, calves, and feet. This improves with rest. Open sores on the lower leg, ankles, or toes. Weak or no pulse in the affected limb. Cold or numb feet. Pale, bluish-colored toes.
What to Do
See doctor.
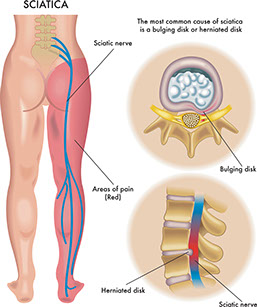
Sciatica
Signs & Symptoms
Sharp pain from the buttocks down the leg. Numbness and tingling in the leg.
Sprain, Strain, or Sport Injury
Signs & Symptoms
Pain in the leg or ankle after an injury that does not keep you from moving the limb.
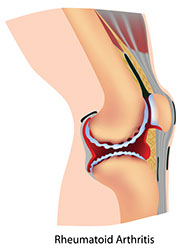
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Signs & Symptoms
Pain, stiffness, and swelling, usually in both knees or ankle joints. The joint looks deformed. Weakness and fatigue. Dry mouth and dry, painful eyes.
Varicose Veins
Signs & Symptoms
Pain or itching in the legs with swollen and twisted veins that look blue and are close to the surface of the skin. The veins bulge and feel heavy. Swelling in the legs and ankles.