Skin Conditions
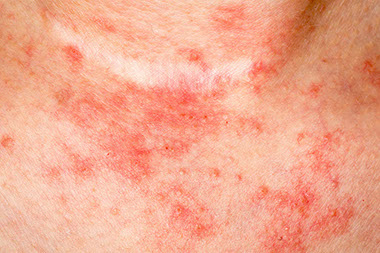
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is a chronic skin condition. It usually appears on the scalp, face, neck, or creases of the elbows, wrists, and knees. It usually improves as you get older, but can be a lifetime problem.
Signs & Symptoms
Patches of skin that are:
* Dry, red, and scaly
* Blistered and swollen
* Sometimes thick, discolored, or oozing and crusting
Causes, Risk Factors & Care
Eczema tends to run in families. It is also more common in persons who have allergies or asthma. Contact with cosmetics, dyes, deodorants, skin lotions, permanent press fabrics, and other allergens can aggravate eczema; so can wool fabrics, stress, exposure to extreme weather conditions, and eating foods, such as eggs, milk, seafood, or wheat products.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for skin infections and/or other medicines if self-care does not relieve symptoms.
Self-Care
* Don’t scratch! This makes eczema worse. Your skin can get infected. Keep your fingernails cut short.
* Don’t take baths too often. Add bath oil to the water. Sponge bathe in between tub baths. Take quick showers.
* Use warm (not hot) water when you take a bath or shower.
* Use a mild soap or no soap at all on the areas of eczema.
* Don’t use wool clothes and blankets.
* Use a light, nongreasy and unscented lotion on your skin after you wash. Don’t use lotions that have alcohol. They can dry the skin.
* Try to keep from sweating. For example, don’t wear too many clothes for the weather.
* Wear rubber gloves when you do housework. Put talcum powder or cornstarch inside the gloves, or use latex gloves lined with cotton.
* Avoid foods, chemicals, cosmetics, and other things that make your eczema worse.
When to Seek Medical Care
Contact Doctor When:
* You have signs of an infection: Fever; and/or large amount of weeping or crusting skin areas.
* Your skin is red, you can’t stop scratching, and this keeps you from sleeping.
* You get no relief from self-care.

