SELF-CARE CORNER

The skin is the largest organ of the body. Yet, it is easy to overlook what is literally right in front of you when you look in the mirror every day.
Regularly examining your skin, including the hard-to-reach places, gives you early notice that you should visit a dermatologist. Catching concerns early makes diagnosis and treatment easier and more effective.
Common conditions
Few people have flawless skin. It’s normal to experience skin issues, and the risk of skin disease increases with age. Common dermatological concerns you may experience include:
* Acne
* Psoriasis
* Eczema
* Rosacea
* Skin cancer
* Nail fungus
* Hair loss
* Wrinkles and other cosmetic skin concerns
Skin Self-exam
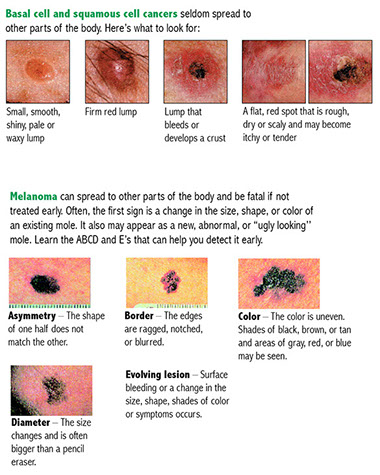
Many skin conditions are highly treatable when caught early. A regular skin self-exam lets you examine your whole body and monitor any moles, blemishes, or areas of concern.
1. Do a skin exam about once a month after exiting the shower or bath.
2. Stand in front of a full-length mirror. Check your front, back, and each side with your arms raised.
3. Bend your elbows and examine your forearms, underarms, and palms.
4. Using a hand mirror, check the back of your neck and scalp. Part your hair to look closer at your scalp.
5. Check your back and buttocks using a hand mirror.
6. Sit down and thoroughly examine your legs, the soles of your feet, and between your toes.
When to seek care
A dermatologist is a medical professional specially trained in diagnosing and treating hair, skin, and nail conditions. Regular visits to a dermatologist should be part of routine adult healthcare. But, in between visits, be on the lookout for these signs:
* A mole or patch of skin that changes color, size, or shape
* Severe or persistent acne
* Rash, itching, or hives that do not clear on their own
* A skin condition that does not heal
* Long-lasting skin irritation
* Persistent dry skin patches
* Nails that appear yellow or brittle
* Increasing hair loss