SELF-CARE CORNER
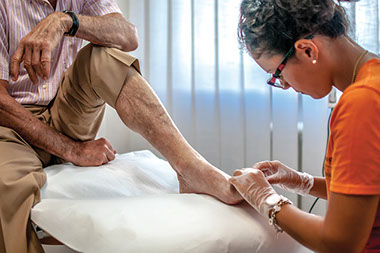
People with diabetes have a higher risk of getting certain foot problems. This usually happens because diabetes can cause nerve damage in the feet. This is known as diabetic neuropathy, which can lead to tingling, burning or weakness in your feet.
Why does neuropathy matter?
Diabetic neuropathy isn’t just painful. It also means that you may not feel things like cuts, injuries or heat or cold on your feet. Your feet could get hurt or burned and you wouldn’t know it. Then, with reduced blood flow, your body may not be able to heal the skin very well.
Keeping skin healthy
Wash, dry and moisturize the skin on your feet every day. Also, check for problems. Here’s how:
* After bathing, dry your feet gently with a towel.
* Look for corns, calluses, blisters or cuts. If you notice any of these, call your health care provider. Don’t try to remove corns or calluses yourself.
* If your skin looks healthy, you can moisturize. Apply a skin cream to dry areas.
* Don’t apply cream between your toes. This can cause fungus to grow. Keep the area between toes clean and dry.
* If you can’t trim your toenails easily, have this done by a podiatrist or other health provider.
Good shoes are your friend
Poorly fit shoes can cause sores, or ulcers, on your feet. These can lead to infection. Even if you don’t feel pain, see your doctor about any sores on your feet. You should also stay off your feet until your doctor says it’s ok. Don’t walk in your bare feet because this can put your feet at risk.
You can avoid many foot ulcers by getting comfortable, supportive shoes. A podiatrist or foot specialist may help you find a pair that fits your feet well without rubbing. Wearing socks that wick moisture, such as wool socks, can also help. Wearing wet socks or shoes can lead to fungal infections.
Helpful ways to avoid foot problems with diabetes:
1. Go to regular checkups.
2. See your doctor if you have any foot injuries or skin changes on your feet.
3. Follow your diabetes plan to keep blood sugar under control.
4. Check your feet every day.
Source: American Diabetes Association
© American Institute for Preventive Medicine