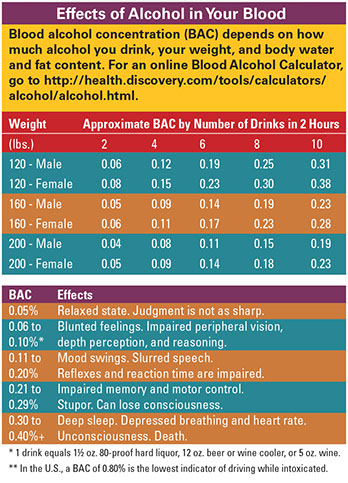
Before drinking, think about its possible consequences (e.g., academic and health problems, unsafe sex, assault, injury, and even death). These consequences affect the person who drinks as well as other students (whether they choose to drink or not) and the community as a whole.
Alcohol Poisoning
Call 9-1-1 for one or more of the following signs of alcohol poisoning or combining alcohol and other drugs, such as sedatives or tranquilizers. Act quickly. Alcohol poisoning can be fatal.
* Unconsciousness. This means the person is hard to rouse and can’t be made aware of his or her surroundings. This can be brief, such as with fainting or blacking out. It can put a person into a coma.
* No breathing or slow and shallow breathing. This means 10 or fewer breaths per minute or time lapses of more than 8 seconds between breaths.
* Slow pulse rate (40 or fewer beats per minute).
* Skin that is cold, clammy, and/or pale or blue in color.
{Note: Before emergency care arrives, place the person on his or her side with the knees bent, to prevent choking if he or she vomits. Loosen the person’s clothing around the neck and check the mouth and back of the throat to see that nothing obstructs the person’s breathing. Stay with the person.}
Alcohol Poisoning
* Choose substance-free housing, if available and desired.
* Be aware and think about the risks and consequences of drinking, including getting arrested, getting sick, contracting an STI, etc. One incident of alcohol use could cause you to do something you will regret for the rest of your life. Alcohol plays a part in most sexual assaults.
* Mixing drinking with driving, drugs, or operating machines can be fatal. Designate a sober driver.
* Not everyone drinks. Be with people who drink non-alcoholic beverages or ones that look like “drinks,” such as non-alcoholic beer in a glass.
* It is better to get medical help for a person who needs it instead of worrying about getting a friend in trouble.
* Drink alcohol only if you want to, and if you do:
– Know your limit and stick to it or don’t drink any alcohol.
– Drink slowly. You are apt to drink less. Have one drink during a party. Take fake sips, if necessary. In reality, anything over two drinks does not increase the feeling of pleasure. Drinking too much leads to being unable to enjoy yourself.
– Eat when you drink. Food helps to slow alcohol absorption.
– Alternate an alcoholic beverage with a non-alcoholic one. Use non-alcohol or reduced alcohol beverages. Dilute distilled beverages. Use more and more mixer and less and less alcohol. After two drinks, your taste buds are dulled and you won’t be able to notice much difference.
– Avoid drinking contests and games.
Resources
Emergency Medical Service (Call 9-1-1) if you suspect alcohol poisoning or a drug overdose
Your school’s Student Health Service, Student Counseling Service, or Alcohol and other Drug Program
Al-Anon/Alateen World Service Office
888.4AL.ANON (425.2666)
www.al-anon.org
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) World Services
www.aa.org
Center for Substance Abuse Treatment (CSAT) National Drug Treatment Referral Routing Service
800.662.HELP (4357)
www.findtreatment.samhsa.gov
Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
818.773.9999
www.na.org
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse & Alcoholism (NIAAA)
www.niaaa.nih.gov
www.thecoolspot.gov