Bone & Muscle Problems
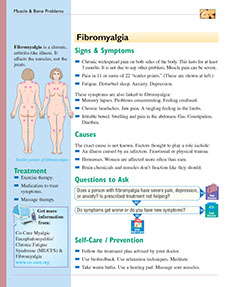
Fibromyalgia is a chronic, arthritis-like illness. It affects the muscles, not the joints.
Signs & Symptoms
* Chronic widespread pain on both sides of the body. This lasts for at least 3 months. It is not due to any other problem. Muscle pain can be severe.
* Pain in 11 or more of 22 “tender points.” (These are shown at right.)
* Fatigue. Disturbed sleep. Anxiety. Depression.
These symptoms are also linked to fibromyalgia:
* Memory lapses. Problems concentrating. Feeling confused.
* Chronic headaches. Jaw pain. A tingling feeling in the limbs.
* Irritable bowel. Swelling and pain in the abdomen. Gas. Constipation. Diarrhea.
Causes
The exact cause is not known. Factors thought to play a role include:
* An illness caused by an infection. Emotional or physical trauma.
* Hormones. Women are affected more often than men.
* Brain chemicals and muscles don’t function like they should.
Treatment
* Exercise therapy.
* Medication to treat symptoms.
* Massage therapy.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
* Follow the treatment plan advised by your doctor.
* Use biofeedback.
* Use relaxation techniques. Meditate.
* Take warm baths.
* Use a heating pad.
* Massage sore muscles.
Resources
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)