BE FIT

When it comes to getting a good workout, no two people are alike. Age, health status, fitness level, and many other factors can play a role in how hard you can – or should – exercise.
Your target heart rate can tell you if you’re exercising hard enough to burn calories, but not too hard. Your target heart rate is how fast you want your heart to beat during exercise.
You can find your target heart rate by following these steps:
1. Get a stopwatch or use a watch or clock that has a second hand.
2. Periodically during exercise, put two fingers on a pulse point. This can be the inside of your wrist on the thumb side, the inside of your elbow, or the side of your neck.
3. Count how many times your heart beats in 60 seconds.
Next, find your age in the chart and see if your heart rate is within the target heart rate zone listed. If it’s higher than the zone, take your workout down to an easier level. If it’s below, you may be able to exercise a little harder.
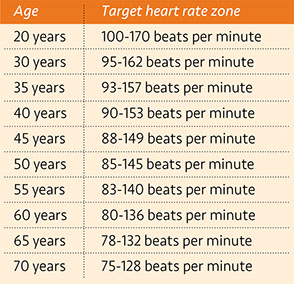
If you’re just starting out with exercise, aim for the lower end of the range. After a few weeks, you can gradually work up to a higher heart rate within the zone.
People who have heart conditions or other health problems should discuss any exercise or fitness activities with their doctor before starting. Certain medications that treat heart and blood pressure disease can cause a lower heart rate. Discuss your medications with your physician before trying to reach your maximum heart rate.
Heart rate and blood pressure explained
Heart rate and blood pressure are not the same thing. Blood pressure is the force of blood moving through your body. Heart rate or pulse is simply the number of times your heart beats per minute.
A faster heart rate does not necessarily mean your blood pressure is rising. When the heart rate speeds up, blood vessels get bigger, allowing more blood to move through. This means many people can safely raise their heart rate during exercise without affecting their blood pressure.
Talk to your doctor about blood pressure and get it checked yearly. Most people with high blood pressure can and should exercise with their doctor’s approval.
Source: American Heart Association


