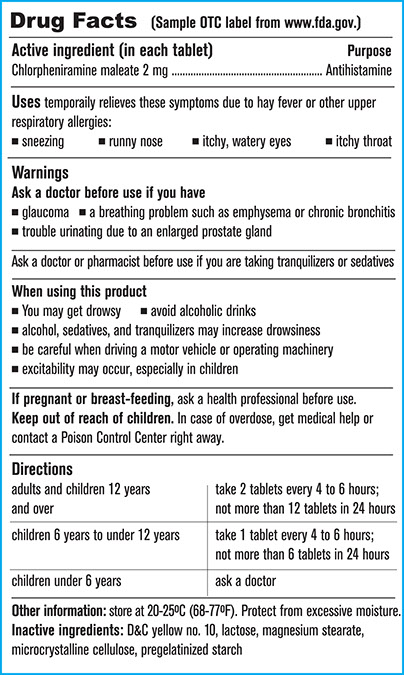
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are ones that you can get without a prescription. Often, they are less potent than prescribed ones. When taken in large amounts, though, an OTC medicine might equal or exceed the dose of a prescribed medicine. Read the information on the label. To learn more about OTC medicine labels, accesswww.fda.gov. Search for “over-the-counter medicine label.”
* Ask your doctor or health care provider what OTC products are safe for you to use and what you should take for pain and fever.
* To prevent harmful side effects and interactions, review all of the OTC medicines, supplements, and herbal remedies that you take with your doctor.
* Do not take OTC medicines on a regular basis unless your doctor tells you to.
* Read the package labels. Heed the warnings listed. If you are unsure whether or not an OTC medication will help or harm you, check with your doctor or pharmacist.
* Store medicines in a dry place and out of children’s reach. Do not call medicine “candy.”
* Before you take a medicine, check the expiration date. Discard expired medicines. Crush pills. Dissolve them in water. Mix this with used coffee grounds or kitty litter and put it in the garbage in a sealed bag.
* If you have an allergy to a medicine, check the list of ingredients on OTC medicine labels. Find out if what you are allergic to is in them. Some labels will warn persons with certain allergies to avoid taking that medicine.
* Do not take any OTC product if you are pregnant or nursing a baby unless your doctor or health care provider says it is okay.
* Before taking herbal remedies and supplements, check with your doctor.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
www.fda.gov