You may already know you should wear sunscreen to decrease your risk of skin cancer and sun damage. In fact, the Skin Cancer Foundation says that wearing sunscreen regularly can decrease your chance of getting melanoma (the deadliest skin cancer) by 50 percent. Wearing sunscreen regularly will also help you avoid signs of aging like wrinkles and dark spots.
But the sunscreen aisle at the store leaves many people feeling overwhelmed. There are so many choices, different labels, numbers and ingredients. How do you choose one?
The best sunscreen is one you like, because you should use it every day, says the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). Here’s how to narrow it down and choose the sunscreen that’s right for you:
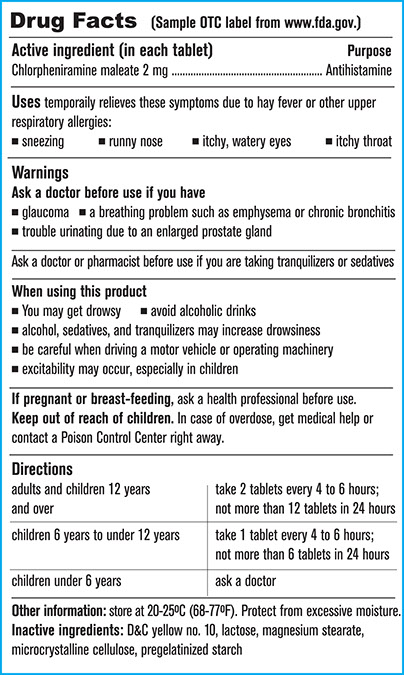
BROAD SPECTRUM
Always look for the words “broad spectrum.” This means it protects against both kinds of UV rays, and it’s important for proper protection.
SPF
Choose an SPF of at least 30.
SPF NUMBERS
Don’t let high numbers fool you. The Skin Cancer Foundation says higher SPF sunscreens do protect more, but not by much. No matter what the SPF number says, you still need to reapply at least every two hours, and always after toweling off, sweating or swimming.
WATER RESISTANT
If you’re going to be sweating or swimming, choose one that says “water resistant.” There is no such thing as “waterproof” sunscreen. The bottle will say how long the sunscreen will remain water resistant. It may say “40 minutes” or “80 minutes.” That’s how often you need to reapply it when you’ve been in the water.
LIPS
Choose a sunscreen for your lips too. A lip balm with broad spectrum SPF 30 is also important. Skin cancer can – and does – affect the lips.
GELS vs CREAMS
Sunscreen gels are great for oily skin, while creams work well for dry skin.
SENSITIVE SKIN
If you have sensitive skin, consider a physical-only sunscreen. This means the active ingredients on the bottle will only include titanium dioxide or zinc oxide, or both. While chemical sunscreens work well, they can irritate some sensitive-skin types.
PRICE TAG
Expensive doesn’t always mean better. A higher price tag may be due to the brand name or certain extra ingredients that make it feel nicer or smell good. It doesn’t mean it will protect you more than a cheaper bottle.
NO COMBINATION
Don’t choose a combination sunscreen and insect repellant. The AAD says sunscreen should be reapplied liberally every two hours. But insect repellant should only be applied lightly every several hours as needed.
BABIES
Most sunscreens are only approved for babies over 6 months of age. Look for a physical-only sunscreen or one formulated for babies. Babies younger than 6 months should be kept in the shade and covered with lightweight protective clothing and hats, says the American Academy of Pediatrics.