Tobacco Cessation
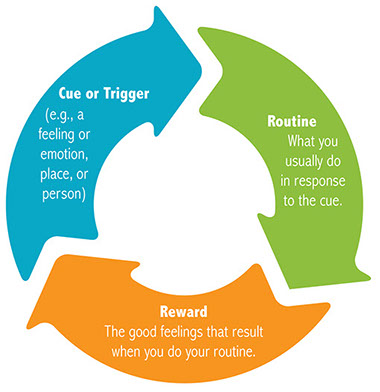
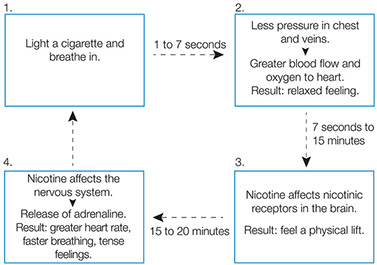
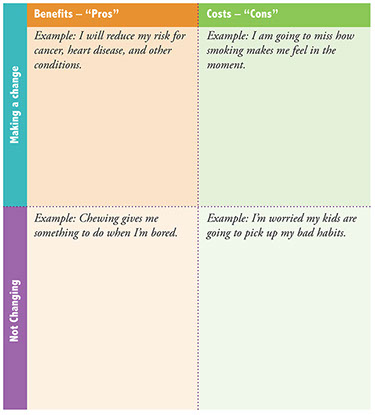
Until lately, many people assumed cigarette smoking was just a bad habit (albeit an unhealthy one). In 1988, the Surgeon General’s Report on Smoking and Health changed that view. After reviewing over 2,000 scientific studies, the report confirmed what many scientists suspected: Smoking cigarettes is addictive, because they contain nicotine. So in order for you to quit smoking, you need to break the physical addiction as well as the psychological habit.
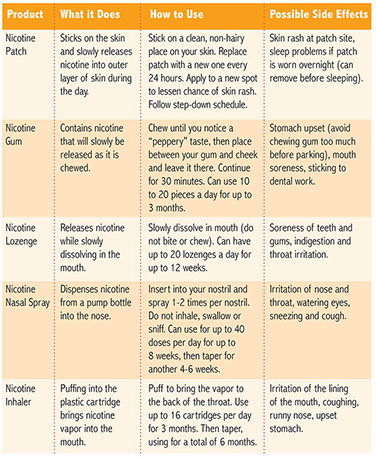
A technique called nicotine replacement therapy can help break that stranglehold. With a nicotine replacement product, smokers absorb small amounts of nicotine. These little doses enable them to reduce their nicotine cravings and wean themselves off cigarettes with little anxiety, irritability, sleepiness, headaches, or other symptoms that make nicotine withdrawal such torture. (Some say nicotine withdrawal is worse than heroin withdrawal-or close to it.)
If you think nicotine replacement therapy might help you to quit smoking:
* Talk to your doctor about prescribed medicines (nicotine inhaler or nicotine nasal spray) or over-the-counter nicotine replacement products, such as a patch, gum, or lozenges.
* Follow all instructions for the product you use.
In order for nicotine replacement therapy to work, a smoker should also follow the kind of behavior modification techniques outlined in the previous tip. Or you can attend a reputable stop-smoking program. Studies have shown that combining a nicotine replacement product with a stop-smoking program can triple your chances for success.