MEDICAL NEWS

Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the U.S. Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, kills one American every 54 minutes.
The good news is many cases of skin cancer can be prevented. Before you head outside to enjoy the sunshine and fresh air, know how you can protect yourself and your family from skin cancer.
*There’s no “safe” tan:Getting a “base” tan before vacation isn’t safe. It increases your risk of skin cancer and aging of the skin. Using self-tanners is the only safe way to get a bronze glow.
*Seek shade:One of the best ways to avoid UV rays is to love the shade. Trees, umbrellas and buildings are easy ways to keep the sun’s rays off your skin, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when rays are strongest.
*Get vitamin D safely:Though the skin makes vitamin D when it’s exposed to the sun, there are safer ways to get what you need of this nutrient. Eggs, fatty fish, fortified dairy and juice are good ways to get your D.
*Use caution with water and snow:Swimming and skiing can expose the skin to more UV rays because the sun reflects off water and snow. Be diligent about sun protection during these kinds of activities.
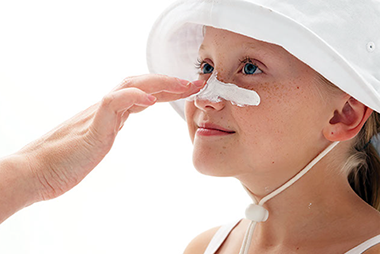
*Apply (and reapply) sunscreen:Use a sunscreen labeled “broad spectrum” with an SPF of at least 30. Reapply at least every 2 hours, and after swimming or toweling off.
*Use protective clothing:Sun protective hats, shirts, scarves and more are available to help block UV rays. Look for clothing and swimwear with a “UPF” rating on the label for protection. Use it with sunscreen for optimum protection.
Finally, contact your doctor if you notice a new, itchy or painful mole. Moles with irregular shapes and borders or those that are black or multicolored should be checked.
Sources: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, American Cancer Society, Skin Cancer Foundation