Causes
* Anxiety, stress, caffeine withdrawal, or depression
* Lack of sleep. Poor sleep position.
* A sensitivity to certain foods and drinks.
* Reading a lot, especially in dim light
* Missing or delaying a meal
* Doing boring work
* Being in one position for a long time, like at a computer
* Hormone changes that come with menstruation, while taking birth control pills, etc.
* Exposure to chemicals and/or pollution
* Side effects from some medications
* Dirty or polluted air
* Airplane travel
* Alcohol
* Poison
* Poor posture
* Cigarette smoke
* Too much physical activity
* Bright lights. This includes watching TV.
* Movement, such as riding in a car or elevator
* Loud noises
* Strong odors
* Eating or drinking something very cold, such as ice cream
Types
You can have cancer for years without having symptoms. There is usually no pain at the onset of cancer. As different types of cancers grow, warning signs may occur. See your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
For Tension or Muscular Headaches
About 90 percent of all headaches are tension or muscular headaches. These headaches respond well to self-care, without causing ongoing problems. Symptoms include:
* You have a dull ache in your forehead, above your ears, or at the back of your head.
* You feel pain in your neck or shoulders.
Tense or tight muscles in the face, neck, or scalp result in these headaches. Common causes are:
* An illness
* Fever
* Tiredness
* Stress
* Worry
* Concentrating hard for long periods of time
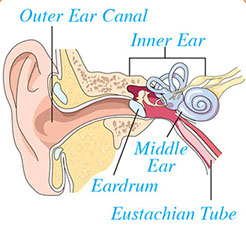
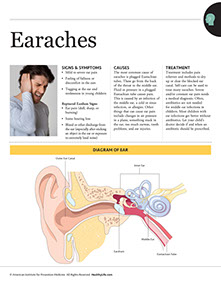
For Sinus Headaches
Symptoms
* The pain is in your forehead, cheekbones, and nose.
* The pain is worse in the morning.
* It hurts more if you bend over or touch your face.
* Your nose is stuffy.
Sinuses are behind your cheeks, around your eyes, and in your nose. You may get a sinus headache from:
* A cold or upper respiratory infection
* Allergies, like hay fever
* Other breathing problems
* Swimming in dirty or polluted water
* Airplane travel
These things interfere with fluid drainage in the nose, causing a buildup of pressure. Pain results.
For Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches usually start at night, can last from 15 minutes to 3 hours, and can interrupt sleep. They can also start during the hours a person is awake. These headaches come once or twice a year, usually in older men, and tend to run in families.
Cluster headaches are much less common than migraines. Spring and autumn are the most common times of the year for them. Symptoms include:
* The pain is on one side of your head.
* The pain is in or on the sides of your eyes.
* Your eyes are watery.
* The pain is sharp, burning, and intense.
* Your pupils look smaller.
* One or both of your eyelids droop.
* You get headaches in groups (clusters), everyday for a week or longer.
For Children’s Headaches
Children’s headaches that come once in a while can be treated with ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Make sure you use the right type and dose for your child’s weight. Don’t give aspirin to anyone younger than 19 years of age due to its link to Reye’s Syndrome. Reye’s Syndrome is a rare disease that can cause death. It usually occurs 7 to 10 days after the onset of the flu or chicken pox. If the child complains of head pain on a regular basis, take the child to his or her doctor. Symptoms:
* The headaches tend to be shorter than ones in adults.
* Sometimes, an upset stomach and vomiting are also present.
* Headaches come in groups, then are gone for months.
For Migraine Headaches
Migraines happen when blood vessels in your head open too wide or close too tight. At least one in eight adults suffer from migraines. Women have migraines more often than men. Migraines tend to run in families, too. Symptoms include:
* One side of your head hurts more than the other.
* You feel sick to your stomach or throw up.
* You may see spots or zigzag flashes of light.
* Light hurts your eyes.
* Noise bothers you.
* Your ears ring.
* Your face is pale.
* After the headache, some people have a drained feeling with tired, aching muscles. Others feel great after the headache goes away.
Types of Migraine Headaches
* Migraines with an aura. An aura is when a person sees spots or flashing lights for 10 to 15 minutes or his or her face becomes numb. (Ten percent of migraines are this type.)
* Migraines without an aura. They start more slowly and tend to last longer than migraines with an aura. They don’t begin with changes in a person’s vision or numbness. (Ninety percent of migraines are this type.)
Prevention
Keep a headache diary. Write down when, where, and why the headaches seem to start. Try to avoid things that trigger headaches.
Be aware of early symptoms. Try to stop the headache as it begins.
* Exercise on a regular basis.
* Keep regular sleep hours, even on weekends.
* Don’t smoke. If you smoke, quit.
* Cut down on salt.
* Avoid excess alcohol. Alcohol can lead to a “hangover” headache.
* Don’t have foods and drinks known to trigger headaches in sensitive people.
Foods and Drinks That May Cause Headaches
* Alcohol, especially red wine
* Bananas (if more than 1/2 banana daily)
* Beans: Broad, lima, fava, snow peas
* Brewer’s yeast
* Caffeine (from coffee, tea, cola soft drinks, some medications, chocolate) or caffeine withdrawal
* Chicken livers, paté
* Citrus fruits (if more than 1/2 cup daily)
* Cured meats (hot dogs, luncheon meats, etc.)
* Figs, raisins, papayas, avocados, red plums (no more than 1/2 cup daily)
* Foods with MSG (monosodium glutamate), such as soy sauce, meat tenderizers, seasoned salt
* Hard cheeses (aged cheddar, provolone, etc.)
* Herring, pickled or dried
* Nuts and peanut butter
* Onions
* Pickled, preserved, or marinated foods
* Sauerkraut
* Sour cream
* Sourdough bread
* Vinegar
Treatment
Usually, headaches are not linked to serious health problems. Self-care treats most headaches.
Self-Care
* Rest in a quiet, dark room with your eyes closed.
* Rub the base of your skull with your thumbs. Work from the ears toward the center of the back of your head. Also, rub gently along the sides of your eyes, your shoulders, neck, and jaw.
* Take a warm bath or shower.
* Place a cold or warm washcloth, whichever feels better, over the area that aches.
* Take an over-the-counter (OTC) medicine (that your provider recommends) for pain. Take it right away.
* Relax. Imagine a calm scene. Meditate or breathe deeply.
Medication
* Over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications. Examples are aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen sodium and ketoprofen. Most tension and muscular headaches go away with OTC medications. Some OTC medicines (e.g., Excedrin Migraine® and Motrin Migraine Pain®) are FDA approved for migraine headaches.
* Prescribed medicines. Examples are:
– Triptan drugs, such as sumatriptan
– Ergotamines, with or without caffeine
– Antihistamines
– Beta-blockers
– Calcium channel blockers
– Tricyclic antidepressants
Take medicines as prescribed.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a process of learning how to control internal functions to relieve pain. Biofeedback training has helped many people who have suffered from headaches.
These things occur with biofeedback:
* A biofeedback therapist explains how the muscles react to stress and cause tension headaches.
* Most of the time, you sit in a comfortable chair in a dimly lit room.
* A headband, connected to a machine, is fastened across your forehead. The machine emits a steady sound that changes if muscles in the head or neck are tensed.
* A small thermometer is attached to one of your fingers. Another machine keeps track of your temperature.
* You learn how to use these biofeedback machines.
* You learn to control the automatic response of your muscles and blood vessels that cause headaches.
* Then you learn to do the same thing without the machines to control headaches on your own.
Medical Care
Reasons to Get Medical Care Fast
* A headache due to a serious head injury or a blow to the head causes severe pain, enlarged pupils, vomiting, confusion, or feeling sleepy.
* Severe pain occurs in and around one eye.
* A severe, persistent headache occurs with a stiff neck or a red or purple rash that doesn’t fade when pressure is applied to the skin.
* The headache came on suddenly and hurts much more than any headache you have ever had.
Call 9-1-1 if signs of a stoke occur:
* A sudden and severe headache with no known cause
* Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
* Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding
* Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
* Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
Reasons to Call Doctor or Health Care Provider
* The headache has lasted more than 2 to 3 days and keeps getting worse.
* Migraine headaches (intense, throbbing, one-sided, often with nausea or vomiting) occur often. Flashing lights or spots may precede the pain.
* A headache persists or recurs and is present with nausea or vomiting.
* A headache started after taking a new medicine (prescribed or over-the-counter).
Work with Your Health Care Provider
For headaches that do not need medical care fast, contact your primary care provider first. Most likely, he or she will be able to figure out the type of headache you have. If not, he or she can refer you to a specialist. Tips on working with your doctor or health care provider:
* Make notes before your office visit.
* List every symptom, even if it seems minor.
* Be honest with your health care provider. The facts you give could be important in finding out why you have headaches.
* Follow your doctor’s advice. Let him or her know if the prescribed treatment helps. Tell your doctor if you have any side effects from treatment.
* Answer these questions before your office visit:
– When did your headaches begin (days, weeks, months, years ago)?
– How long does your headache last (minutes, hours, days)?
– How often do you have these headaches (once a day, once a week, etc.)?
– Where does it hurt (both sides, one side, etc.)?
– How does the pain feel (dull, sharp, throbbing, nonstop)? How does the pain usually start (dull or sharp)?
– Is there a pattern to your headaches? Are they gone for months at a time then come back several times a day? Are they worse lately?
– Are your headaches different from each other? (You may have more than one kind.)
– When does the pain usually start (at night, in the morning)?
– Are there any symptoms just before the headache begins (stuffy nose, pain elsewhere, flashing lights)?
– Do any other symptoms occur with the headache (upset stomach, pain elsewhere)?
– What helps the headache go away (rest, medicine, hot or cold treatment, massage)?
– Does anything make the pain worse (moving the head, standing or lying)?
– Does an activity or situation bring on headaches (after exercise or eating a certain food)?
– Are you taking any other medicines or drugs?
– Is another health care provider treating you for anything else?
Resources
National Headache Foundation
800.843.2256
www.headaches.org