Children’s Health
Colds and flu are infections of the nose and throat. Both are caused by viruses.
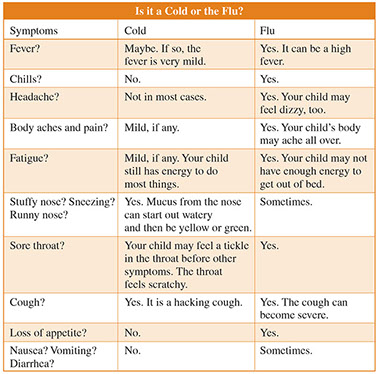
It can be hard to tell if your child has a cold or the flu. Why? They both have the same type of symptoms. But symptoms for the flu are worse than ones for a cold. Flu symptoms come on fast. Ones for a cold come on slower.
Signs & Symptoms
Prevention
Antibiotics do not treat colds and flu. Most colds clear up in about a week. Sometimes, a cold lasts up to 2 weeks.
Fever and most flu symptoms usually go away after 5 days, but coughing and feeling weak can last up to 2 weeks.
To Help Prevent Colds and Flu
* Take your child for a yearly flu vaccine as advised.
* Don’t smoke or let your child smoke.
* Keep your child away from persons who have the flu or a cold.
* See that your child eats and sleeps well and gets lots of exercise.
Tell your child to do these things:
* Wash your hands often. Keep them away from your nose, eyes, and mouth.
* Cover your nose when you sneeze. Use a handkerchief or tissues when you sneeze, cough, or blow your nose. This helps prevent passing germs to others.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care
Have your child do these things:
* Rest.
* Drink lots of liquids. They help clear out the respiratory tract. This can help prevent other problems, like bronchitis.
* Eat chicken soup. It helps clear out mucus.
If your child’s throat is sore, have him or her do these things:
* Gargle every few hours with 1/4 teaspoon of salt in 1/2 cup of warm water, if able to. (A child can usually do this starting at age 6.)
* Suck on a piece of hard candy or cough drop once in a while. (Don’t give these to children under 5 years old.)
Things you can do:
* Try to clear your child’s nose. This is very important in babies under 6 months old, because some can’t breathe through their mouths yet. Also, they can’t breast or bottle-feed if they can’t breathe through the nose. To clear your child’s nose:
– Use an over-the-counter spray or drops for the nose made of salt and water. An example is Ocean® brand. Follow the label’s advice or that of your child’s doctor.
– For a baby who can’t blow his or her nose, leave the salt drops in for 1 minute. Then use a soft rubber suction bulb to draw out the mucus. Lie the baby on his or her back. Aim the bulb straight down, not at an angle! (You can get a suction bulb at the drug store.) Or use a cotton swab to wipe the mucus out. Don’t put the suction bulb or cotton swab too far into the nose. You could cause a nosebleed.
– For a child who can blow his or her own nose, have the child do it 1 minute after the salt drops are in.
* Put a cool-mist vaporizer or humidifier in your child’s room. Use distilled (not tap) water. Clean it every day.
* For fever and muscle aches, give your child acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Make sure you give the right kind and dose for your child’s weight. (Note: Do not give aspirin. Aspirin and other medicines that have salicylates have been linked to Reye’s Syndrome.
* Check with your child’s doctor about using over-the-counter medicines for colds and flu for children under age 2.
* Call your child’s doctor if he or she gets a fever after a cold or after the flu has gone away.
* Washing the hands often helps stop spreading the flu. Have your child wash his or her hands:
– After playing with others.
– When he or she gets home from school.
– After blowing his or her nose.
– After touching toys or other people’s things.
Signs of Reye’s Syndrome
Be on the lookout for Reye’s Syndrome after the flu or chickenpox. Reye’s Syndrome does not happen very often. But you should know about it. Look for these signs:
* Vomiting over and over again. Or vomiting that does not stop.
* Loss of pep and energy.
* Acting very, very sleepy.
* Acting very, very cranky.
* Striking out at others.
* Acting strange.
* Convulsions.
(Note: If your child shows signs of Reye’s Syndrome, get medical care fast!)