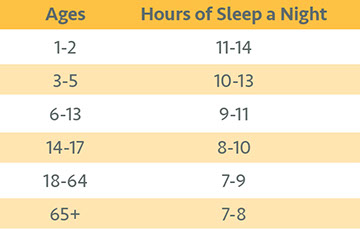
Insomnia includes problems falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. It is normal to have a bad night of sleep every now and then. Occasional poor sleep becomes insomnia when this pattern continues for several weeks AND fatigue or feeling drowsy during the day occurs due to lack of sleep.
There are many causes of insomnia. Too much caffeine, travel, taking care of an ill loved one, or stress can affect your sleep. Quite often, insomnia is a result of conditioning your body to be awake in bed, even if you feel tired or know you need sleep. Having trouble sleeping over several nights may lead to worrying about being able to fall asleep or expecting to lie awake for hours.
Whether your sleep issues are transient (come and go) or chronic (occur all the time), this guide can help to improve your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Sleep Problems & Health Conditions
If you have trouble sleeping or have daytime sleepiness for longer than three weeks, consult your doctor.
Any condition, illness, injury, or surgery that interrupts sleep due to pain, discomfort, or waking to urinate can cause sleep problems. Health conditions that affect sleep include: arthritis, asthma, COPD, fibromyalgia, narcolepsy, and thyroid disorders. Sleep problems are also linked to many mental illnesses. These include anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, PTSD, and substance abuse. Over-the-counter medicines, such as decongestants and diet pills can affect sleep, too.
Sleep Apnea Signs:
* Loud snorting sounds while sleeping on the back
* Repeated periods when breathing stops for 10 or more seconds during sleep
* Waking up many times during the night and excessive daytime sleepiness
* Exhaustion and having a hard time concentrating during the day
Periodic Limb Movements in Sleep (PLMS) and Restless Leg Syndrome Signs:
* Creeping, crawling, pulling and/or painful feelings in one or both legs
* Jerking or bending leg movements that you can’t control during sleep