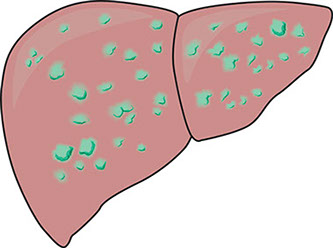
Hepatitis is liver inflammation. With hepatitis, the liver has trouble screening poisons from the blood. Also, the liver can’t regulate bile. This is a liquid that helps digest fats.
Signs & Symptoms
Signs and symptoms depend on the cause. Some persons have no symptoms. When symptoms first occur, they include fatigue, fever, appetite loss, nausea and vomiting, and joint pain.
Later, symptoms are dark urine, pale, clay-colored stools, and jaundice. This is a yellow color to the whites of the eyes and/or the skin.
Causes
One or More Types of Viral Hepatitis
* Hepatitis A. This is spread through food or water contaminated by the feces of an infected person that has the virus.
* Hepatitis B. This is caused by contact with infected blood or bodily fluids from an infected person. Examples are sharing drug needles or having sex. A mother can pass this virus to her baby during childbirth, too.
* Hepatitis C. Most often, the cause is contact with infected blood on needles, razors, toothbrushes, etc. Blood transfusions given before July, 1992 could be the cause, if the blood had the virus. Sexual contact may spread the virus, too.
* Hepatitis D. Sharing drug needles or having sexual contact with an infected person can cause this type, but only in persons who already have hepatitis B. It is not common in the U.S.
* Hepatitis E. This is caused by contact with food, water, or something contaminated with the feces of an infected person. This type is not common in the U.S. It is more common in Africa and India.
Non-Viral Causes of Hepatitis
* Some immune system disorders, such as Wilson’s disease. With this, too much copper is stored in the liver and other body organs.
* Chronic alcohol or drug use.
* Reaction to certain medicines. One example is long-term use or an overdose of acetaminophen. Heavy drinkers are more prone to this.
* Some herbs may cause hepatitis. Examples are kava and chaparral.
In some cases, the cause is not known.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of hepatitis and how severe it is. For non- viral forms, this includes treating the disorder or stopping the use of the substance that caused it. For viral forms, treatment includes self-care measures and medications.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
To Help Prevent Hepatitis A and E
* Get a hepatitis A vaccine if advised by your doctor or health department. There is no vaccine for hepatitis E.
* When you travel to countries where the virus is widespread, wash your hands often. Drink boiled water. Don’t eat unpeeled or uncooked fruits or foods rinsed with water. Don’t use ice.
* If exposed to hepatitis A, contact your doctor to get immune globulin (IG) within 2 weeks of exposure.
To Help Prevent Hepatitis B, C, and D
* Get 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine if advised by your doctor. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
* Practice Safer Sex.
* Don’t share IV drug needles.
* Don’t share razors or toothbrushes. See that sterilized items are used for ear piercing, etc.
To Help Prevent Non-Viral Forms
* Use alcohol in moderation, if at all.
* Don’t combine alcohol and acetaminophen. Take products that contain acetaminophen, such as Tylenol, as directed. Heed warnings listed on the label.
To Treat Hepatitis
* Follow your doctor’s advice for medicines, etc.
* Rest.
* Drink at least 8 glasses of fluids a day.
* Avoid alcohol and any drugs or medicines that affect the liver, such as acetaminophen.
* Follow a healthy diet. Take vitamins and minerals as advised by your doctor.
Resources
National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention
800.CDC.INFO (232.4636)
www.cdc.gov/nchhstp