Skin Conditions
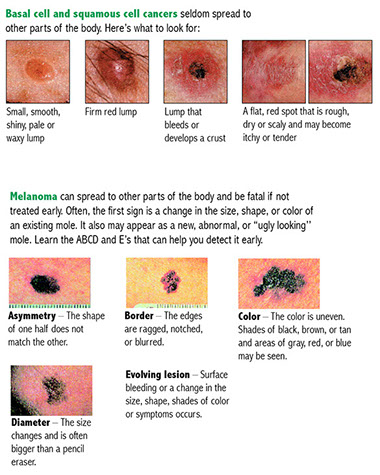
Age spots are skin blemishes that come with aging. All age spots are generally harmless. They are more a cosmetic issue than a medical one. It is important, though, to distinguish them from skin cancer.
Signs & Symptoms
* Small or large, flat, freckle-like marks that are different shades of brown (liver spots). These most often appear on the arms, backs of hands, back, face, or shoulders.
* Brown or yellow slightly raised spots (seborrheic warts)
* Red, pinpoint blemishes (cherry angiomas)
Causes
Aging skin is thinner and more sensitive to the sun’s rays. Small, dark patches appear in response.
In general, age spots do not need medical treatment. A doctor can freeze an age spot with liquid nitrogen or remove it in a minor surgical procedure, if skin cancer is suspected.
Prevention
Reduce exposure to the sun. When you are outdoors, use a sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 15 or higher.
Self-Care
To Help Make Age Spots Less Noticeable:
* Avoid sun exposure.
* Try a bleaching cream.
* Apply lemon juice twice a day to age spots.
* Dab buttermilk on spots and lightly pat dry.
* Use fresh aloe gel on spots. Do this twice a day for a month.
* Use a mild, moisturizing make-up.
When to Seek Medical Care
Contact Doctor When:
* You suspect the spots are skin cancer.
* An age spot bleeds, itches, or tingles.
* You have bothersome age spots that resist fading after using self-care.
* You want advice on removing age spots; on creams with the medicine Retin-A; or on chemical peels.







_web-crop-u253859.png)