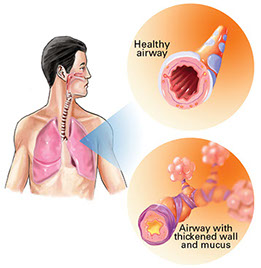
The letters COPD are for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This is lung disease that worsens over time. With COPD, airways are narrowed and blocked. The lungs are damaged. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe in and out. In the U.S. and throughout the world, COPD is a major cause of illness and death. Most often, COPD is due to one or both of these problems:
* Chronic bronchitis. This causes swelling and the build-up of mucus in the lungs.
* Emphysema. This damages the walls of the air sacs in the lungs.
Signs & Symptoms
* A chronic cough. The cough brings up mucus or phlegm.
* Shortness of breath. This is usually worse with exercise or when you exert yourself.
* Feeling like you can’t take a full, deep breath
* Chest tightness
* Wheezing. This is a whistling sound when you breathe.
* Frequent colds and other respiratory infections
* Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet
Symptoms of COPD usually start after 40 years of age and slowly worsen over time.
Diagnosis
COPD is usually diagnosed with a breathing test called spirometry. Spirometry measures how much air your lungs can hold and how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. It is a simple and fast test. Your doctor or nurse technician will ask you to take a deep breath and then breathe out as hard and as fast as you can into a mouthpiece. The spirometer will measure and record the results.
A chest X-ray or CT scan can also diagnose COPD. Sometimes, a blood sample is taken to test levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
Causes
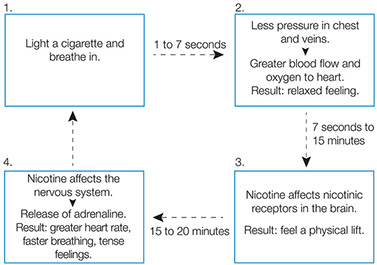
* Smoking. This is the main cause. More than 90 percent of people with COPD are smokers or former smokers.
* Breathing in other lung irritants over a long period of time. These include air pollution and dust or chemicals used in the mining and textile industries.
* In some rare cases, having a genetic disorder called Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. This is due to a defective protein in the blood.
When to Seek Medical Care
Reasons to Call Your Health Care Provider
* You have a much harder time catching your breath.
* You have sudden tightness in your chest.
* You cough a lot more, it becomes difficult to cough, or you cough up yellow, green, brown or red-colored mucus.
* You have a fever.
* You have heart palpitations or a faster pulse than usual.
* You have a sudden increase or loss of appetite.
* You have blurry vision or see double.
* You become unusually dizzy or sleepy or you can’t think clearly.
* You are anxious or depressed.
Reasons to Get Emergency Care
* Your lips or fingernails are blue or gray.
* It is hard for you to talk or walk.
* Your breathing is fast and hard, even after taking medicine.
* Your heart is beating very fast or irregularly.
Prevention
The best way to prevent COPD is to not smoke. If you smoke, commit to quit! Talk to your doctor about over-the-counter or prescribed medications that can help you quit. To increase your chances of success, take part in a stop smoking class or program.
* Avoid secondhand smoke and other lung irritants.
* If you work in an at-risk industry, wear protective clothing and equipment. Follow the safety measures of your workplace.
You can get help to quit smoking from:
1-877-44U-QUIT (448-7848)
1-800-QUIT-NOW (784-8669)
www.lungusa.org
www.smokefree.gov
Treatment
Work with your health care provider to develop and follow a treatment plan to meet your needs.
Medications
* Bronchodilators relieve shortness of breath and keep airways open.
* Anticholinergics relax airway muscles.
* Inhaled steroids reduce swelling in the airways.
* Antibiotics and antiviral drugs treat infections that occur with COPD and that make it worse.
Oxygen Therapy
Your doctor may prescribe oxygen therapy if oxygen levels in your blood are too low. Oxygen is provided by an oxygen cylinder or concentrator and delivered through a nasal tube. It can help you be more active and lead a better life.
* Use your oxygen, as advised by your doctor or care specialist.
* Do not smoke or let people around you smoke while oxygen is in use.
* Before you travel, ask your doctor how to have your oxygen needs met. Discuss where you plan to go and your method of travel. If you are flying, check with the airline for rules about traveling with oxygen. You may need a letter from your doctor or copies of your oxygen prescription, so plan ahead.
Vaccines
People who have COPD are more likely to be sicker longer and may have more serious health problems when they get the flu or pneumonia.
* Get a yearly flu shot. Get information fromwww.cdc.gov/fluor 1-800-CDC-INFO (232-4636).
* Get a pneumonia vaccine, as advised by your doctor.
* Lower your risk of illness. Wash your hands often with soap and water and keep them away from your eyes, nose, and mouth. When you can’t wash your hands, use alcohol-based hand cleaners. Avoid crowded places when possible.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
You work with a team of health care providers to create a personal treatment plan and set goals. You learn to manage your COPD to live a more normal life. Pulmonary rehabilitation includes:
* Exercise. This strengthens your muscles and improves your endurance. It makes it easier for you to move, do activities, and take care of yourself. You will find out how often to exercise, for how long, and how hard to push yourself.
* Emotional Support. Many people who have COPD also deal with depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Some programs offer emotional support, group counseling, and/or relaxation training.
* Disease Education. You will learn how to quit smoking, eat healthy, and manage symptoms.
Self-Care
Quit smoking! This is the most important thing you can do to manage your COPD.
Learn your triggers and know how to avoid them.
* Don’t smoke.
* Control household triggers, such as dust. Wear a filter mask when you vacuum, dust, and do hobbies or work that involve dust and other irritants. Use a damp (not dry) cloth for dusting.
* Keep your home well-ventilated.
* Do not use aerosols, ammonia, lye, kerosene, powders or solvents. Find out about products that are safe for you and the environment at Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) House atwww.epa.gov/iaqandwww.epa.gov.
* Stay inside when air quality is poor. Find Air Quality Index forecasts fromwww.airnow.gov.
* Follow your health care provider’s advice for using air filters and air purifiers.
Manage your coughing.
* Do not take over-the-counter cough or other medicines unless your doctor tells you to. Your health care provider can teach you techniques for coughing comfortably and productively.
* Unless you are told by your doctor to limit your fluids, drink at least 8 glasses of water a day to keep mucus thin and easier to cough up.
Practice pursed lip breathing to relieve shortness of breath:
* Relax. Close your mouth. Breathe in through your nose. Do this slowly and count: one, two.
* Purse your lips like you are going to whistle. Breathe out slowly and count: one, two, three, and four.
* Do not do this tight-lipped.
Resources
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America
800.7.ASTHMA (727.8462)
www.aafa.org
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
301.592.8573
www.nhlbi.nih.gov