People who smoke just a few cigarettes a day are exposed to the same serious health risks as heavier smokers, breaking a common myth that social or casual smoking is somehow safe or that they can easily quit.
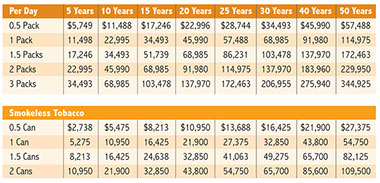
Casual smokers who smoke between 1 and 4 cigarettes a day, are tripling their risk of dying of heart disease and lung cancer, according to Dr. Robin J. Mermelstein, a clinical psychologist and director of the Center for Health Behavior Research at the University of Illinois at Chicago who specializes in smoking cessation counseling. Light smokers represent about 7 million of the U.S. smoking population.
For light smokers looking to quit and stay smoke-free, Dr. Mermelstein offers the following advice:
*Think about the reasons you smoke.It will give you a clearer path to quitting. Does smoking relieve stress? Is it a large part of your social life?
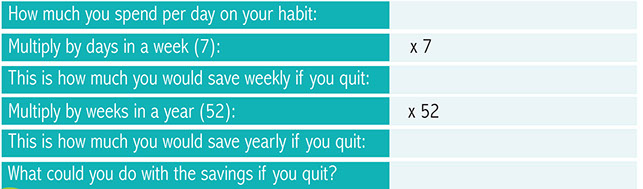
*Get your head in the game.Get support products like nicotine replacement therapy and online help. Customized online support services provide encouragement to help you break your behavioral and psychological link to cigarettes and is proven effective in helping smokers quit.
*Choose nicotine replacement that’s right for you.Lighter smokers may be less likely to use nicotine replacement therapy to help them quit, which means they could be setting themselves up for failure. Nicotine replacement therapies are clinically proven to reduce the physical withdrawal symptoms like cigarette cravings and can double a smoker’s chance of quitting successfully.
For light smokers or heavier smokers, research shows the most successful approach to quitting is a combination of medicine, such as nicotine replacement patches, that can help reduce the physical cravings of nicotine, and behavioral strategies that help smokers cope with those triggers to light up. Your employer may offer some of these options.