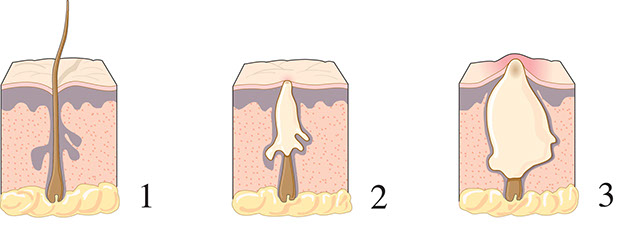
A number of vaginal problems occur in women over age 50. Often, the problems are due to changes in the vagina that come with menopause. These include:
* Vaginal dryness
* Thinning of the walls of the vagina
* Loss of elasticity in the muscles in the vagina
* Shrinkage of the labia (external genitals that cover and protect the opening of the vagina)
These changes can lead to common vaginal problems, such as:
* Pain during and after intercourse
* Vaginitis – vaginal swelling, irritation, and/or infections.
Less common vaginal problems in women over 50 are:
* Sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
* Cancer of the vagina, which is rare.
* Abnormal vaginal bleeding (unless still menstruating or on hormone therapy (HT)
It is common for menstrual periods to be irregular for several years before menopause. This is normal vaginal bleeding. For premenopausal women, the most common causes of abnormal vaginal bleeding, in this order, are: Not ovulating; malignancy; pregnancy; endometriosis; and benign tumors. The most common cause after menopause is malignancy.
The chart below lists signs and symptoms of vaginal problems and what to do about them. {Note: All vaginal bleeding that occurs after menstruation has stopped should be evaluated by your doctor.}
Hemorrhage
Signs & Symptoms
Vaginal bleeding with:
* A known bleeding disorder and you also have blood in your urine or stool
* Heavy vaginal bleeding after taking a clot dissolving drug for a heart attack or stroke
What to Do
Get immediate care.
Internal Injury
Signs & Symptoms
Vaginal bleeding after trauma to the abdomen, pelvis, or vagina or vaginal bleeding with any of these problems:
* Dizziness and very heavy bleeding (you saturate more than 1 full sized pad in an hour’s time)
* Pale and moist skin and a decreased level of consciousness
* Extreme shortness of breath or a very hard time breathing
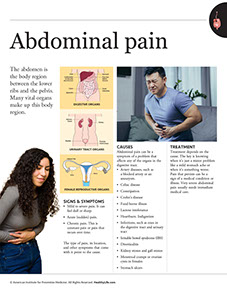
* Severe abdominal pain
What to Do
Get immediate care.
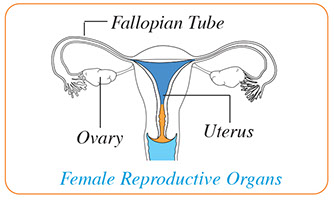
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
This is an infection of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and/or ovaries.
Signs & Symptoms
Vaginal bleeding with 2 or more of these problems:
* Abdominal tenderness and/or bloating
* Pain in the pelvis or back
* Pain during intercourse
* Skin on your abdomen feels sensitive
* Vaginal discharge with abnormal color or odor
* Change in menstrual flow, if still menstruating
* Fever, chills
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Infection of the cervix, uterus, or vagina
Cervical, uterine, or vaginal cancer.
Signs & Symptoms
Vaginal bleeding after menopause, unless on estrogen therapy (ET).
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Gonorrhea or similar sexually transmitted infection (STI)
Signs & Symptoms
Abnormal vaginal bleeding with:
* Mild itching and burning around the vagina
* Burning or pain when urinating or urinating more often
* A vaginal discharge with abnormal color
* Abdominal discomfort
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Genital Herpes
Signs & Symptoms
Sores and/or painful blisters in the genital area and sometimes on the thighs or buttocks
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Trichomoniasis
Signs & Symptoms
* Vaginal itching, burning, and redness
* Greenish-yellow vaginal discharge
* Burning or pain when urinating
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Bacterial Vaginosis
This is an infection from one or more types of bacteria that may or may not be sexually transmitted.
Signs & Symptoms
* Mild vaginal irritation or burning
* A thin, gray, or milky white vaginal discharge. This has a fishy odor, which is noticed more after sex. (About half of females have no symptoms.)
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Atrophic Vaginitis
This is caused by a decrease in estrogen.
Signs & Symptoms
Vaginal dryness, irritation, itching, and burning
What to Do
Contact doctor.
Vaginal Yeast Infection
Signs & Symptoms
* Itching, irritation, and redness around the vagina
* Thick, white vaginal discharge that looks like cottage cheese and may smell like yeast
* Burning and/or pain when urinating or with sex
What to Do
Use self-care.
Vaginitis from Contact Dermatitis
Signs & Symptoms
Itching and redness in the outer genital area without other symptoms
What to Do
Use self-care.
Care
Medical treatment depends on the cause.
For Atrophic Vaginitis:
Use a prescribed estrogen cream or prescribed estrogen pills.
For Bacterial Vaginosis:
Use a prescribed antibiotic cream or gel or prescribed antibiotic pills.
For a Vaginal Yeast Infection:
It is important, though, to make sure that you have the right problem diagnosed. A burning sensation could be a symptom of a urinary tract infection caused by bacteria, which requires an antibiotic. Antibiotics will not help yeast infections. They make them worse. Trichomoniasis mimics yeast infections, too.
Chronic vaginal infections can be one of the first signs of diabetes, sexually transmitted diseases, or HIV in women.
Self-care measures treat most vaginal yeast infections. Your doctor can prescribe a vaginal cream or suppositories or an oral antifungal medicine, such as Diflucan.
For a Severe Case of Contact Dermatitis in the Vaginal Area:
Use an ointment prescribed by your doctor.
Other medical treatments are treating the specific cause, such as STIs, cervical cancer, and uterine cancer.
Self-Care / Prevention
For a Vaginal Yeast Infection or Bacterial Vaginosis:
* Bathe or shower often. Clean the inside folds of the vulva. Dry the vaginal area well.
* Wipe from front to back after using the toilet.
* Wear all-cotton underwear.
* Don’t wear garments that are tight in the crotch.
* Change underwear and workout clothes right away after sweating.
* If you still menstruate, use unscented tampons or sanitary pads and change them often.
* Don’t use bath oils, bubble baths, feminine hygiene sprays, or perfumed or deodorant soaps.
* Don’t sit around in a wet bathing suit.
* Shower after you swim in a pool to remove the chlorine from your skin. Dry the vaginal area well.
* Eat well. Include foods that contain live cultures of “lactobacillus acidophilus,” such as yogurt. If you can’t tolerate yogurt, take an over- the-counter product that contains lactobacillus acidophilus.
* Let your doctor know if you tend to get yeast infections whenever you take an antibiotic. He or she may have you also take a vaginal antifungal agent.
When You Have a Vaginal Yeast Infection:
* Use an over-the-counter product for vaginal yeast infections, such as Monistat, Gyne-Lotrimin, etc.
* Douche with a mild solution of 1 to 3 tablespoons of vinegar mixed in 1 quart of warm water. Repeat only once a day (up to 7 days) until the symptoms subside. Don’t do this if you are pregnant or if you have a sexually transmitted disease.
* Limit sugar and foods with sugar.
For Vaginal Dryness and Painful Intercourse:
* Don’t use deodorant soaps or scented products in the vaginal area.
* Use a water soluble lubricant, such as K-Y Jelly, Replens, etc. Avoid oils or petroleum-based products.
* Use an estrogen cream for the vagina. Your doctor needs to prescribe this.
* Keep sexually active.
* Don’t use antihistamines unless truly needed.
For Contact Dermatitis in the Vaginal Area:
* Avoid products that cause the problem (scented items, douches, etc.).
* Apply an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream to the affected area. Use this infrequently, though. Hydrocortisone can, itself, lead to thinning of the vaginal tissue. Follow package directions.
* Put a cool compress on the affected area.
* Wash your underwear in a gentle detergent. Rinse it twice. Use only plain water for the second rinse. Don’t use a fabric softener.