Abdominal & Urinary Conditions
Kidney stones are hard masses of mineral deposits formed in the kidney(s). They can be as small as a tiny pebble or an inch or more across. They are more common in men.
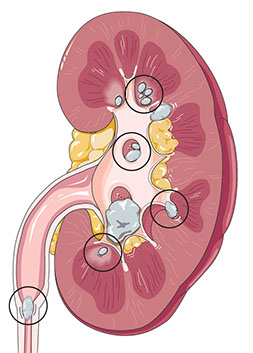
Kidney Stones
Signs & Symptoms
Some kidney stones cause no symptoms. Small ones can be passed, without pain, when you urinate. When symptoms occur, they include:
* Crampy pain that comes and goes. The pain starts in the lower back, travels down the side of the abdomen, and into the groin area. The pain can be severe.
* Bloody, cloudy, or dark-colored urine.
* You may need to pass urine often. You may pass only small amounts of urine. You may only be able to pass urine in certain positions.
* Nausea and vomiting. Fever and chills (if an infection is also present).
Causes
* Too much calcium in the urine or in the blood.
* High levels of uric acid in the blood.
* A diet high in oxalic acid. This is in spinach, leafy vegetables, rhubarb, and coffee.
* Repeated urinary tract infections.
* Mild dehydration that persists.
* Family history of kidney stones.
* Living in certain parts of the U.S. Areas of the southeast have the highest rates.
In some cases, the cause is not known.
Treatment
If the stone is small and can be passed in the urine, treatment may be just drinking plenty of fluids. For stones too large to be passed, lithotripsy using ultrasound is a common treatment. With this, shock waves are directed to the stone location and break the stone into fragments. Drinking fluids helps flush the fragments from the person’s system.
Questions to Ask
Self-Care / Prevention
* Drink lots of fluids. Drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of water a day.
* Eat a well-balanced diet. Vary food choices.
* Save any stone you pass in your urine. Take it to your doctor. Its contents can be analyzed. Follow your doctor’s advice to prevent and treat kidney stones.