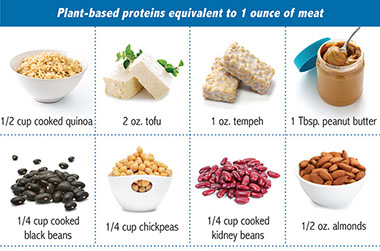
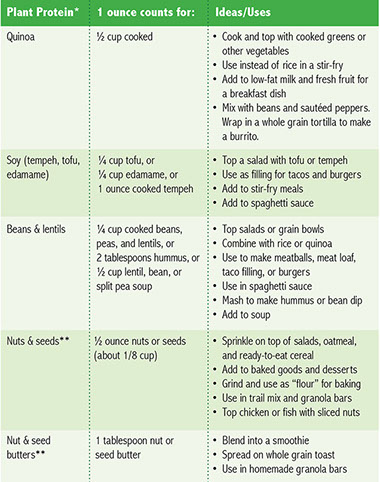
Part 2

Sugars are naturally present in many foods, including fruit, dairy, and grains. Your body can get all the sugar you need by digesting these foods. Sometimes, sugar is added during the processing of foods and drinks. Sugar adds calories, taste, and shelf-life to a product, but zero nutrients. There is no need for added sugars in your diet.
Too much added sugars is associated with:
* Heart and blood vessel problems. This can lead to fatty liver disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and kidney disease.
* Gut bacteria damage.
* Skin problems like irritation and acne.
* Headaches, aching limbs, and fatigue.
* Nervous tension, anxiety, and depression.
* Tooth decay and gum disease.
* Memory problems and memory loss. This can lead to Alzheimer’s (research ongoing).
Sugar is Addicting
It is okay to have a piece of chocolate every now and then and experience a little “lift” in the brain. Your brain activates dopamine, the brain chemical that gives you a “feel good” feeling. However, eating sugar too often can have addictive effects on the brain.
Impulsive behavior, lack of control, and cravings can result. Your tolerance for sugar may also increase, especially if you are eating or drinking super-sweet artificial sweeteners with hundreds of times the sweetness of regular sugar.
Over time, it becomes harder to control how much sugar you eat. Without fiber, healthy fats, and other nutrients that help you feel full, your natural “stop eating” system is hijacked. Sugar addiction leads to overeating, a highway to obesity.
Hooked on Sugar:The pathway below shows how your body can become addicted to sugar.
* You eat a high sugar food. It tastes good, especially when combined with a fatty or salty food. Addiction pathways are activated in your brain. You feel a rewarding sensation.
* Your blood sugar spikes. Hormones are released to lower your blood sugar.
* Your blood sugar drops rapidly. Your body notices low blood sugar levels.
* You feel hungry and crave food, especially sugary foods. Your body thinks you are starving and demands sugar.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition that makes it difficult for the body to properly get energy from food. Risk factors include family history and being overweight. Insulin, a hormone made in the pancreas, works like a key to a door, allowing sugar to go from the bloodstream into the cells.
In addition to extra body weight, eating too much sugar (and foods that break down into sugar like bread and pasta) puts a strain on your pancreas to work harder. Over time, this means too much sugar stays in the bloodstream, which causes serious problems for your blood vessels, heart, and brain.
Diabetes should be managed carefully to control blood sugar levels. If you already have type 2 diabetes, losing weight, following a healthy eating plan, and doing regular exercise can help you manage diabetes and may reduce the need for medication.
Be a Label Detective: Find the Added Sugar
How can you tell if a product has added sugars? Find a food package or drink bottle and follow the steps below.
Step 1: Check the Nutrition Facts
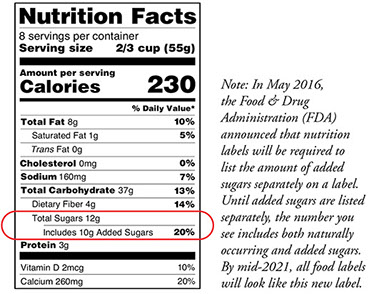
Step 2: Check the Ingredients List
Read the ingredients list on a processed food’s label to tell if the product contains added sugars. There are many names for sugar. Some words you might find in a list of ingredients that indicate a sugar include:
* Sugar
* Syrup
* Nectar
* Juice
* Malt
* Molasses
* Honey
* Words that end in “-ose”
Honey, maple syrup, molasses, brown rice syrup & stevia may be better choices among sugars. However, limit all added sugars.
If a sweetener is one of the first 3 ingredients on the label, avoid this product. It may be high in calories but not include many nutrients.
Step 3: Find out the real amount
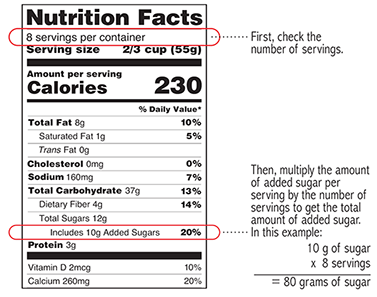
If you have more than the serving size listed on the label, you are getting even more sugar than the label says. If you have half of the serving size, you will get half of the sugar listed.
How much added sugar is okay?
It is almost impossible to avoid all added sugar. Sugar is added to nearly every processed food. Yogurt, salad dressing, ketchup, crackers, peanut butter, tomato sauce, and most bottled beverages contain added sugars.
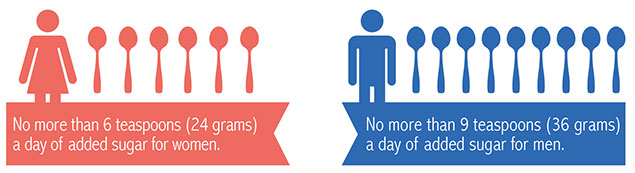
The American Heart Association has set recommended limits on daily intake of added sugars:
Reduce Sugar-Sweetened Drinks
Sugar-sweetened drinks (including pop/soda, bottled tea and coffee drinks, juices, flavored waters, etc.) are some of the top sources of added sugars in the U.S. By choosing water or unsweetened drinks, you can reduce added sugar and calories, leaving room in your diet for nutrient-dense foods.
* What is one sugar-sweetened drink you consume now?
* Look at the label. How many grams of sugar does it contain per serving?
If you drink sweetened beverages, you will very likely go over your daily limit for added sugar.
What about Bottled Fruit Juice?
100% fruit juice is more nutritious than soda, as it often contains vitamin C and may be fortified with calcium. However, fruit juice does not contain fiber to slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Instead, squeeze a lemon or orange slice into plain water. Or, have the whole fruit for a serving of heart-healthy fiber and a naturally sweet treat!
Look for Hidden Sugar Traps
Many foods you wouldn’t consider “sweets” contain a lot of added sugar. Find each of the food products below and check the Nutrition Facts. You may already have these products at home. Or, check next time you are in the store. For the product you are looking at, check how many grams of sugar are in this food. Would you typically only eat one serving?
* Yogurt
* Salad dressing
* Tomato sauce
* Ketchup
* Bread
* Cereal
* Granola bars
What changes do you need to make to get your total added sugar below the number of teaspoons advised for your gender?
Careful!“Low Fat” or “Lite” foods, other than dairy foods and drinks, often make up for taste and texture with sugar and artificial ingredients. Foods that are “sugar free” may have artificial sweeteners and other chemicals to make the product still taste sweet. Choose these foods less often.
More Ways to Limit Added Sugars
* Add a slice of lemon, lime, or cucumber to water for a flavorful twist.
* Avoid buying sweet snacks or candy. Mentally practice passing by and not stopping to pick up sweets at the store or vending machine.
* Add your own natural sweetener, if needed, such as whole, dried, or canned fruit (packed in water or 100% juice).
* Toast whole grain bread to bring out natural sweetness.
* Schedule 30 minutes of physical activity and 30 minutes more sleep each night for a natural energy lift.
* Limit foods high in added sugars as occasional treats.
* Add fresh or canned fruit (packed in water or 100% juice) to plain yogurt instead of having yogurt that contains added fruits and sugar.
* Avoid rewarding children with sweets. Ask relatives and friends not to reward your child with sweets.
* Buy bread from your local bakery. These breads may have fewer added sugars.
* Make your own cakes, pies, and cookies. Reduce the sugar in the recipe by one-third or more. Use baking swaps.
* Order a child-size dessert or split a dessert.
* Cut back on added sugar in coffee and tea. Each week, cut the amount of sugar you add to these drinks by half until you add no sugar.
Be realistic!Enjoy sweet treats, but make these foods “once in a while” foods. Savor and enjoy treats when you do have them. Eat them slowly and pay attention to the taste, texture, and pleasure from the food.