Osteoporosis is a loss in bone mass and bone strength. Bones become less dense. This makes them weak and easier to break. Any bone can be affected. The hips, wrists, and spine are the most common sites.
Signs & Symptoms
Osteoporosis is a “silent disease.” It can occur without pain. You don’t see or feel changes taking place inside your bones. Often, the first sign is a fracture of the hip, wrist, or spine. When signs and symptoms occur, they include:
* Gradual loss of height
* Rounding of the shoulders
* Sudden back pain
* Stooped posture
* Dowager’s hump
Causes & Risk Factors
Bone is living tissue. It breaks down and is replaced with new bone. Osteoporosis occurs when new bone does not replace old bone fast enough.
Risk Factors
* Being female. Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men.
* Low estrogen level. This occurs with menopause.
* Low testosterone level in men
* Aging
* A family history of osteoporosis or broken bones as adults
* Having a thin, small-framed body
* Lack of exercise, especially weight-bearing ones, such as walking and dancing
* Long-term bed rest
* Low calcium and vitamin D intake or absorption
* Smoking
* Drinking too much alcohol
* Long term use of some medicines, such as oral corticosteroids and antacids with aluminum
* Having certain health problems, such as anorexia nervosa, an over-active thyroid gland, and rheumatoid arthritis. Persons with Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease are at an increased risk, too.
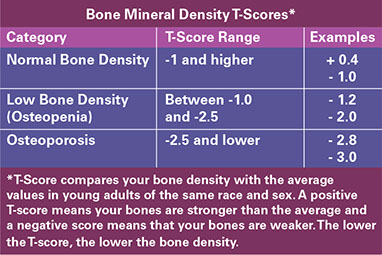
Diagnosis
There is no cure for osteoporosis. The focus is to:
* Prevent the disease
* Prevent further bone loss
* Build new bone
* All women 65 years of age and older should have a bone mineral density (BMD) screening test. Women who have had a fracture or are at a high risk for osteoporosis should get this test sooner than age 65, as advised by their doctors.
* Older men should have a BMD test if they have key risk factors for BMD-related fractures:
– A past fracture, possibly due to osteoporosis
– Low body weight. Physical inactivity.
– Prolonged use of corticosteroid medications.
{Note: Follow your doctor’s advice for when and how often to get screening tests for osteoporosis.}
* The most common test used to measure how dense bones are is a special X-ray known as a DXA or DEXA scan. You lie on a table and a technician moves a scanner above your spine, hip, or wrist. This safe and painless test takes about 10-20 minutes. Test results can identify persons who are at the highest risk for fractures.
Medical Care
Talk about your bone health with your doctor. Discuss:
* Your personal and family medical history
* Medications you take and have taken
* Falls or broken bones you have had as an adult
* Self-Care / Prevention measures you do already and ones you need help with
Medical treatment may include:
* Treatment for problems that increase the risk for low bone mass and osteoporosis
* Evaluating your risk of falls. Tests for this include ones that check your balance, vision, blood pressure, muscle strength, and heart rhythm.
* An exercise program for your needs. Physical therapy may be prescribed.
* High doses of vitamin D if your blood level is very low. Your doctor needs to prescribe this.
* Medications:
– Some slow down the breakdown of old bone. Two categories of these are bisphosphonates (biss-FOSS-fuh-nates) and anti-resorptive agents. Some of these medications are pills. Others are given in shots or through an IV.
– Another one (teriparatide) helps the body make new bone faster than the old bone is broken down.
Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of medications. Find out what side effects you should let him or her know about.
Reasons to Contact Doctor/Provider
* You have any “Signs & Symptoms” of Osteoporosis.
* You want to find out about medicines and other ways to prevent and/or treat osteoporosis.
* You are a female age 65 or older and have not had a bone mineral density (BMD) test.
* You are a female age 50 and older; you have had a fracture or are at high risk for osteoporosis; and you have not had a BMD test.
* You are an elderly male; you have risk factors for osteoporosis; and you need advice on getting a BMD test.
* After a fall, bump or strain, you have wrist, hip, or back pain.
* After a fall, you are not able to get up. Call or have someone call 9-1-1!
Self-Care / Prevention
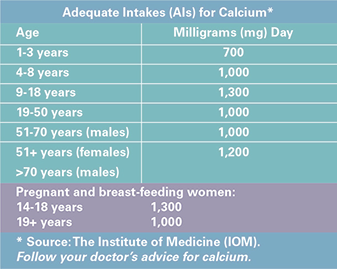
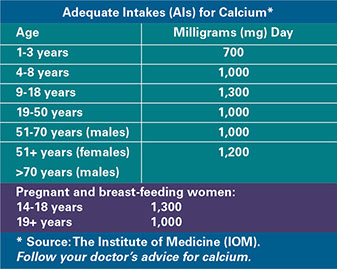
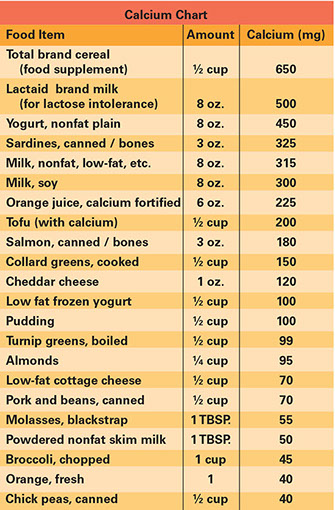
Get Your Recommended Adequate Intake (AI) for Calcium Every Day
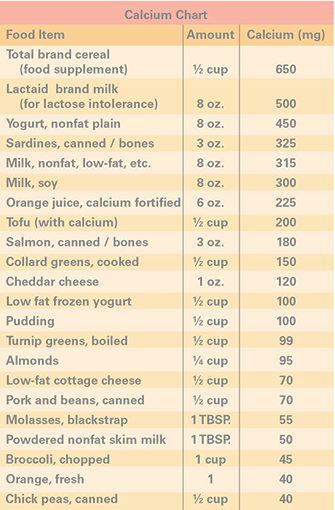
* Choose high-calcium foods daily. Examples are milk, yogurt, salmon, and green leafy vegetables.
* Take calcium supplements, as advised by your doctor. It is best to limit calcium to 500 milligrams at a time. Ask your doctor about taking Tums® to get calcium.
* Eat a balanced diet. Have at least 5 fruits and vegetables every day. These have many vitamins, minerals, and anti-oxidants that can benefit bone health, as well as overall health.
* Don’t smoke. If you smoke, quit! Get help from your doctor,www.smokefree.gov, and/or 1.800.QUIT.NOW (784.8669).
* Limit alcohol. Too much alcohol interferes with the body’s need for calcium and vitamin D. It also increases the risk for falls.
* Take medications, as prescribed.
Sources of vitamin D:
* Sun exposure (without sunscreen) on your skin. Fifteen minutes of midday sunshine may meet the daily need. {Note: You may not get vitamin D benefits from the sun: During winter months; if you have dark skin; and/or you are age 60 years and older.}
* Foods, such as fortified milks and cereals, egg yolks, saltwater fish, and liver.
* Vitamin D supplements, as advised by your doctor. The best source of vitamin D for bone health is vitamin D3.
Use Fall Prevention Measures
(Falling is what leads to broken bones for many people with osteoporosis.)
* Ask your doctor if any medications you take could cause you to fall and how to deal with this. Find out how to deal with vision and balance problems, too.
* Put salt or kitty litter on icy sidewalks. Or stay home during bad weather!
* Use grab bars and safety mats, etc. in your tub and shower.
* Use handrails on both sides of stairways.
* When you reach for things on the floor or pick things up, bend at your knees, not at your waist.
* Wear flat, sturdy, nonskid shoes.
* If you use throw rugs, use ones with nonskid backs. Or tack them down to the floor.
* Use a cane or walker, if necessary.
* Keep halls, stairways, and entrances well lit. Use night lights in hallways, bathrooms, etc.
* Keep a flashlight next to your bed.
* Practice proper posture.
In the house, carry a cordless or cell phone with you, if you can. Doing this keeps you from rushing to answer the phone when it rings. You will also be able to call for help if you do fall.
Be Physically Active
Physical activity throughout life is important for bone health. Putting stress on your bones tells your body that your bones need to be made stronger.
* Do regular, weight-bearing exercise. Do this at least 3 or 4 times a week. Examples are walking, dancing, and step aerobics.*
* Do resistance exercises to strengthen muscles and build bone.* Examples are using weights and resistance bands.
* Do exercises that increase flexibility.* Examples are tai chi, yoga and stretching exercises.
* (Note: A person with osteoporosis should follow the exercise program outlined by his or her doctor.)
Low bone mass and osteoporosis pose a major health threat.
* One out of every 2 women and one in 4 men over age 50 will have an osteoporosis-related fracture in his or her lifetime.
* After a fracture, persons are more likely to have chronic pain, a fear of falling, and depression. They lose independence and have a lower quality of life.
* One year after a hip fracture, 1 in 4 people dies, 1 can’t walk, and 2 of the 4 can walk but are less mobile than before the fracture.
* In the U.S., costs for osteoporosis and related fractures have been estimated to be about $14 billion a year.
Resources
National Osteoporosis Foundation
800.231.4222
www.nof.org
NIH Osteoporosis and Related Bone Disease National Resource Center
800.624.BONE (624.2663)
www.bone.nih.gov