MEDICAL NEWS

Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness for people over 60, so it’s important to know what you can do about it.
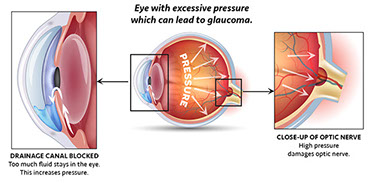
Glaucoma happens when too much fluid builds up in the eye. This extra fluid causes pressure that damages the optic nerve. This damage cannot be undone once it happens. It can lead to loss of all or part of your vision. But, glaucoma can be managed and the damage to vision can be decreased with proper medical care.
People at highest risk for glaucoma
Anyone can get glaucoma. But certain groups of people may be more likely to get it, including:
* People with a family history of glaucoma
* African Americans over age 40
* Anyone over age 60, but Mexican Americans are especially at risk
* People who have high eye pressure, thin corneas or optic nerve problems
* People with high blood pressure that’s not well controlled
Signs and symptoms
Glaucoma often doesn’t have early signs and symptoms until damage has already been done. That’s why getting regular eye exams is so important. For many people, the first sign of glaucoma is loss of their peripheral (side) vision.
Don’t assume you don’t have glaucoma because your eyes “feel fine.” Many people develop glaucoma without any symptoms.
What can you do about glaucoma?
Glaucoma has no cure, but there are things you can do to slow it down and save your vision:
* If you have glaucoma, take your medicines every day. Ask your eye doctor how often you need to be seen, and stick to your appointments.
* Get a complete eye exam at least every 2 years or as often as recommended. This includes a dilated eye exam.
* Even if you don’t have glaucoma, ask your eye doctor about your risk. This includes telling your doctor about any family history of glaucoma.
People with certain risk factors for glaucoma may be given special eye drops. These drops can lower the risk of getting glaucoma but they must be used regularly to be effective.
If you are diagnosed with glaucoma, you and your doctor will discuss what treatment is best for you. It may depend on what type of glaucoma you have and how severe it is. Treatments may include:
* Eye drops that lower pressure in the eye
* Surgery done with a laser that helps the eye drain fluid better
* Traditional surgery that may include placing a new drainage tube in the eye
Save your sight – see your eye doctor to get checked for glaucoma!
Sources: American Academy of Ophthalmology, National Eye Institute