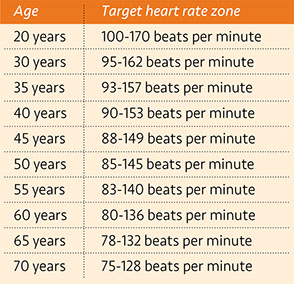
WORK LIFE

You’re bound to run into many different personality types at the workplace. And when you’re working as a team, it can be challenging to adjust to different work styles.
The American Management Association says teamwork leads to better problem solving and productivity. But it’s not as simple as just saying you’re part of a team. Here are some tips to help you achieve the best possible outcome with your group:
*Use your strengths.People have different talents and skills that make them who they are. Offer to use your unique strengths to help get things done. Don’t wait to be asked; volunteer to help when you can.
*Don’t place blame.When things don’t go well, it’s usually not helpful to blame someone else. Instead, look at the problem and work together to find ways to solve it.
*Listen without talking.When others have ideas or opinions, listen to their side before jumping in with your thoughts. Listen with the goal of understanding their point, not adding your own.
*Be aware of different work styles.You may be on a team with someone who does things differently than you. Instead of trying to correct them, see if you can learn something from their way of doing things.
*Be dependable.The best team players are those who get things done on time. Missing deadlines could cause trouble for others on your team or jeopardize your project.
*Communicate.If you’re running into problems or have too much on your plate, tell your team about it. Someone else may be able to help so you can keep the project running smoothly. People may have no idea you’re struggling – unless you speak up and tell them.