MEDICAL NEWS
Your blood is made up of many different types of cells. These include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. White blood cells protect the body from harmful substances and prevent infections.
Blood cancer is caused by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal white blood cells. The abnormal cells do not work properly, preventing them from carrying out their essential functions. As the dysfunctional cells accumulate in the blood, they crowd out healthy cells.
It’s important to know what signs and symptoms to look for. Be sure to check with your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about blood cancer.
Three main types of blood cancer
Leukemia
Leukemia is cancer that affects the bone marrow where blood cells are made. From the bone marrow, it spreads to the blood and can affect other organs.
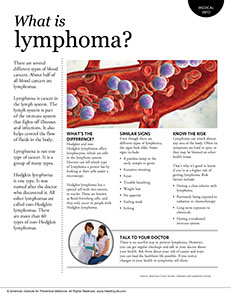
Lymphoma
This type of blood cancer impacts the white blood cells in the lymphatic system. There are two types of lymphoma: Hodgkin, which spreads directly from one lymph node to another, and Non-Hodgkin, which spreads erratically through the lymph nodes.
Multiple myeloma
Myeloma affects plasma cells. These are white blood cells that produce antibodies to fight infections. When the plasma cells don’t function correctly, the body’s immune system doesn’t work properly.
Symptoms of blood cancer
Talk to your doctor if you experience the following:
* Fatigue
* Fever
* Unexplained weight loss
* Bone pain
* Swollen lymph nodes
* Frequent infections
Survival rates have steadily increased
Fifty years ago, there were few successful treatments for blood cancer. Now, there is a range of treatment options available, and more people achieve remission than ever before. Early detection and improved treatments have increased five-year survival rates and provide hope for the future.