The medical name for high blood pressure is hypertension (hy-puhr-TEHN-shun). High blood pressure (HBP) is when blood moves through the arteries at a higher pressure than normal. The heart strains to pump blood through the arteries.
Signs & Symptoms
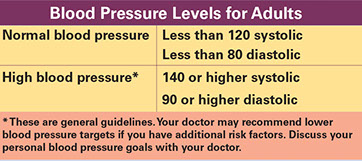
High blood pressure (HBP) is a “silent disease.” Often there are no signs or symptoms. A lot of adults with HBP do not know they have it. So, get your blood pressure checked at each doctor’s office visit, at least every 2 years, or as often as your doctor advises. When blood pressure is 180 or higher (top number) or 120 or higher (bottom number), these signs of a hypertensive crisis may occur:
* Severe chest pain
* Severe headache with confusion and blurred vision
* Severe anxiety
* Shortness of breath
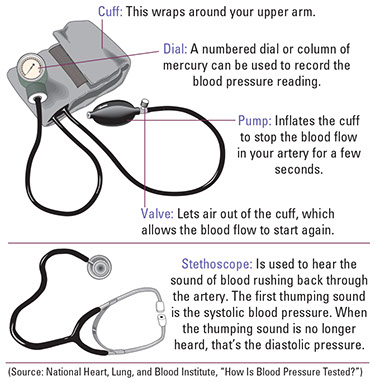
Blood pressure is measured with 2 numbers. The first (top) number measures systolic pressure. This is the maximum pressure against the artery walls while the heart is pumping blood. The second (bottom) number measures diastolic pressure. This is the pressure between heartbeats when the heart refills. The results are given as systolic over diastolic pressure, such as 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
Tips When You Have Your BP Measured
* Don’t drink coffee or smoke 30 minutes before having your BP read. (Don’t smoke at all!)
* Go to the bathroom before you get it checked.
* Before the test, sit for 5 minutes.
* Wear short sleeves so your arm is exposed.
* When you get tested: Sit; keep your back and arm supported; and keep your arm at heart level.
* An average of 2 readings from BP tests taken at least 5 minutes apart should be done.
Causes, Risk Factors & Care
The exact cause is not known.
Risk factors include:
* Family history of HBP
* Aging. More than half of older adults have HBP.
* Smoking cigarettes
* Race. African Americans are more likely to have HBP than Caucasians.
* Gender. Men are more likely to have HBP than women (until women reach menopause).
* Being inactive. Obesity. Sleep apnea.
* Drinking too much alcohol
* Too much sodium intake in some persons
* Emotional distress
High blood pressure could be caused by another medical problem or be a side effect of some medicines. This is called secondary hypertension. This can usually be reversed when the problem is treated.
Diagnosis
Blood pressure readings tell if your blood pressure is high. A health care professional measures blood pressure during an office visit with a manual or automated device called a sphygmomanometer (sfig’-mo-ma-nom-e-ter). The numbers on the gauge measure your blood pressure in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
You should get 2 or more readings at different times. To confirm a diagnosis of HBP, your doctor may have you wear a device that records your blood pressure every 20-30 minutes over a period of 24 to 48 hours. This is called ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM).
Note: Sometimes just being at the doctor’s office is enough to raise some people’s blood pressure. This is called “white-coat hypertension.” If you think this affects you, tell your doctor. You may be advised to check your blood pressure with a home testing device. Your doctor may have you wear a device that records your blood pressure for 24 hours. This will give accurate readings of your blood pressure.
Health Problems Related to HBP
High blood pressure plays a major role in these health problems:
* Stroke. Dementia. Brain damage.
* Heart disease. A person with HBP is 5 times more likely to have a heart attack than a person without HBP. It can also cause the heart to enlarge. This could cause (congestive) heart failure.
* Chronic kidney disease
* Kidney failure
* Vision loss. This includes blindness.
Why is ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) done?
During an office visit, a short-term rise in blood pressure can be due to:
* Emotions or stress
* Pain or physical activity
* Caffeine or nicotine
* “White-coat hypertension.” With this, just being at a doctor’s office or in the presence of medical staff is enough to raise blood pressure.
Getting blood pressure readings over 1-2 days during normal activity and sleep gives a more accurate measurement of your blood pressure.
Self-Care / Prevention
For blood pressure control, follow a healthy lifestyle.
* Get your blood pressure checked at each office visit, at least every 2 years, or as often as your doctor advises.
* Get to and/or stay at a healthy weight. Aim for a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9. Find your BMI using the table below or from:www.nhlbisupport.com/bmi.
* Don’t smoke. If you smoke, quit.
* Limit alcohol to 2 drinks or less a day if you are male and 1 drink or less a day if you are female or age 65 or older.
* Limit caffeine.
* Exercise. Try to do at least 60 minutes a day.
* Learn to handle stress. Take classes. Learn relaxation techniques, etc.
* Take medicine as prescribed. Tell your doctor if you have any side effects, such as dizziness, faintness, or a dry cough without having a cold. Don’t stop taking your prescribed medicine or change the dose(s) unless your doctor tells you to.
* Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you take antihistamines and decongestants. Discuss all prescribed and over-the-counter medicines with your doctor and pharmacist before you take them to avoid harmful drug interactions. Find out about drug and food interactions, too. Ask if grapefruit juice can cause harmful effects with the medicine(s) you take.
* Keep track of your blood pressure using a home testing device. Do this if advised by your doctor.
Medical Care
High blood pressure usually lasts a lifetime, but can be treated and controlled. If you are diagnosed with high blood pressure, follow your doctor’s advice. Medical treatment includes:
* A physical exam and lab tests. These check for damage to your heart, kidneys, and other organs. They also identify risk factors you have for heart, kidney, and other diseases. Your treatment plan is based on your needs.
* Follow-up blood pressure checks and other tests as needed.
* Healthy lifestyle changes.
* Medications. Most persons need more than 1 medicine to treat high blood pressure.
Your doctor will decide if and what medication(s) you need. This is based on your blood pressure level, age, race, other conditions you have, heart disease risk factors, etc. Common medicines used to treat HBP are:
* Diuretics (water pills)
* Calcium channel blockers
* ACE inhibitors
* Angiotensin II receptor blockers
* Beta-blockers
* Alpha blockers. Alpha-beta blockers.
* Nervous system inhibitors
* Vasodilators
Reasons to Get Medical Care
* You have signs or symptoms of a hypertensive crisis. Get medical care right away.
* You need to schedule office visit appointments to get your blood pressure checked. Do this as often as your doctor advises.
* You have adverse side effects from taking medicine(s) to lower blood pressure. Examples are:
– You feel lightheaded or dizzy.
– You feel weak, sleepy, and/or drowsy.
– Your heart races.
– You get a skin rash.
Resources
American Heart Association
800.242.8721
www.heart.org
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
www.nhlbi.nih.gov