It’s the season for colds and flu – and that means coughing. Coughing is an important function in your body. It helps clear your airways. Many times, a mild cough will go away on its own. But when should you see a doctor about a cough?
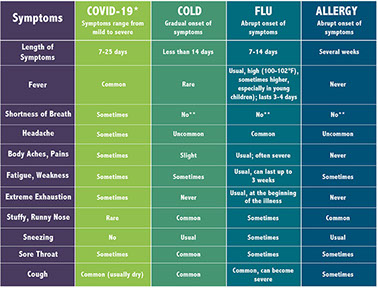
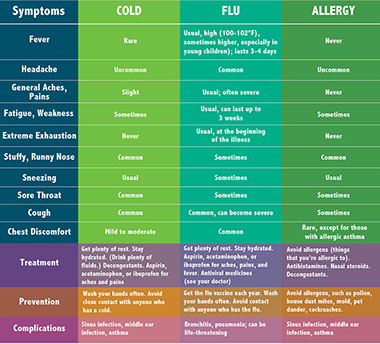
Common cold
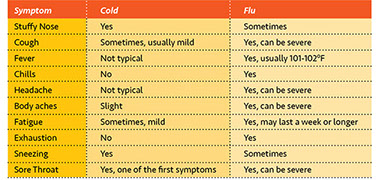
A common cold may cause some coughing. When you have a runny nose, the fluids drain down your throat. This causes your cough reflex to kick in. It’s a way your body protects your lungs. Although a cough from a cold can be annoying, it usually goes away quickly. Antibiotics won’t help with a cough related to a cold.
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation in the tiny tubes in the lungs. These tubes are called bronchioles. Viruses and bacteria can get into the bronchioles and make you sick. Chemicals and toxins like tobacco smoke can also invade the bronchioles and lead to bronchitis.
Symptoms of bronchitis include:
* Coughing, especially with mucus
* Wheezing or feeling short of breath
* Low fever
* Chest pain
Bronchitis is most often caused by a virus so antibiotics will not help. Rest, drinking more fluids and a humidifier can help you feel better.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection in the air sacs inside the lungs. These sacs are called alveoli. Pneumonia can range from mild to serious. If you have pneumonia, you may notice:
* Cough with greenish, yellow or bloody mucus
* Fever, sweating and chills
* Trouble breathing
* Stabbing chest pain that hurts when you cough or take a deep breath
* Loss of appetite
* Feeling weak or tired
* Nausea and vomiting (common in small children)
Many times, a doctor will give you antibiotics for pneumonia. Be sure to take them exactly as your doctor tells you. Pneumonia can be life-threatening if it is not treated effectively.
Pertussis (Whooping cough)
Pertussis is very contagious. It may seem like a cold at first. People may have a runny nose or mild cough.
As it gets worse, pertussis causes a severe cough that can last weeks or even months. The cough makes a high-pitched “whoop” sound. It’s especially dangerous for babies and people with weak immune systems.
The best way to protect against pertussis is to get vaccinated. If you aren’t sure whether you’re vaccinated, ask your doctor. Pertussis is treated with antibiotics.
Sources: American Lung Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute