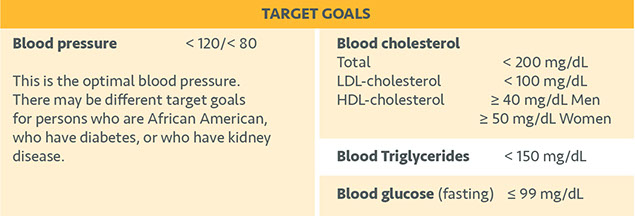
MEDICAL NEWS

Our understanding of cancer has expanded rapidly in recent decades. As a result, cancer treatment continues to improve. However, prevention and early detection are important steps to fight cancer.
Identifying breast cancer before it has the chance to spread is one of the best ways to improve breast cancer survival. In general, the earlier cancer is diagnosed, the better the prognosis. Mammograms are a critical tool for early detection.
How a mammogram works
A mammogram is an x-ray specially designed to look at breast tissue. The amount of radiation exposure from a mammogram is low, and the benefits usually outweigh any risk.
While the images from a mammogram cannot tell you if you have cancer, they can show if there is abnormal tissue in the breast. The presence of abnormal tissue could indicate the need for further testing.
When used as a routine screening tool, a mammogram may detect breast cancer before it presents any symptoms and while it is too small to feel.
When to get a mammogram
A woman’s risk of breast cancer increases over their lifespan. Past a certain age, a mammogram should be a regular part of routine healthcare.
If and when you should get a mammogram is a decision to be made in consultation with your doctor. The general guidelines for women are:
* Women who are 50-74 years of age and at average risk of breast cancer should have a mammogram every two years.
* Women between the ages of 40-49 may benefit from early screening if recommended by their doctor.
* Women at high risk of breast cancer should talk to their doctor about how often to get a mammogram.
Recent Advances in Mammography
The FDA recently approved a computer-assisted and detection (CAD) program to aid doctors in identifying and diagnosing breast cancer using data from mammographies. The advances in CAD have the potential to improve the early detection of breast cancer. This could mean a big step forward in the fight against breast cancer.