Nearly 1 in 4 deaths in the U.S. is due to cancer. In the U.S., the lifetime risk for developing cancer is:
* Slightly less than 1 in 2 for men
* A little more than 1 in 3 for women
What is Cancer?
* Cancer is a broad group of diseases.
* All types of cancer begin when cells in a part of the body start to grow out of control and become abnormal.
* These extra cells may form a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor.
* The tumor destroys healthy tissue.
* If the tumor gets bigger, it can invade and grow into other tissues and organs.
* Cancer cells also can break away and spread through the lymphatic system or blood stream to other parts of the body. This is called metastasis.
* Tumors that are not cancer are called benign. They do not grow into other tissues. They cannot spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors can cause problems, especially if they grow very large and press on healthy tissues and body organs, but they almost never threaten life.
* Untreated cancers can cause serious illness and even death.
Warning Signs & Symptoms
You can have cancer for years without having symptoms. There is usually no pain at the onset of cancer. As different types of cancers grow, warning signs may occur. See your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
For Bladder Cancer
* Blood in urine
* Pale yellow-red colored urine to bright red urine
* Frequent urination or feeling the need to without being able to urinate
* Pain during urination
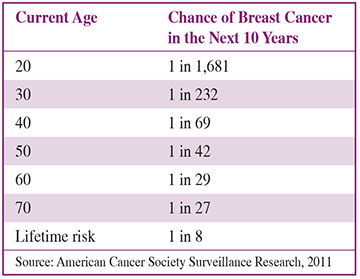
For Breast Cancer
* Lump or firmness in your breast or under your arm
* A change in the size or shape of your breast
* A nonmilky discharge from the nipple. Sometimes this has blood.
* Inverted or tender nipple
* The skin on a breast, areola, or nipple may be scaly, red, or swollen.
* An area of the breast may retract or pucker.
Discuss with your doctor the pros and cons of doing monthly breast self-exams and how to perform them. Ask, too, about your risk for breast cancer. You can also call 800.4.CANCER (422.6237) or accesswww.cancer.gov/bcrisktoolfor the Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool.
Note: Men can get breast cancer, too, and should report a breast lump or other change to their doctors.
For Colon and Rectal Cancers
* Rectal bleeding or red or dark blood in or on the stool. Very narrow stools.
* Change in bowel habits for 2 or more weeks or constipation or diarrhea for 1 week or longer
* Frequent gas pains, cramps, bloating, or feeling of fullness in the abdomen
* Feeling that your bowel does not empty completely
* Weight loss with no explanation
For Kidney Cancer
* Blood in urine
* Lump or mass on the side or lower back
* Low back pain on one side (not due to an injury)
* Weight loss without trying
* Fever that doesn’t go away after a few weeks and that is not from an infection
* Feeling very tired
* Swelling of the ankles and legs
For Lung Cancer
* Cough that gets worse or does not go away. Hoarse voice. Coughing up blood or rust-colored phlegm
* Shortness of breath. New onset of wheezing.
* Chest pain. Often, this worsens with taking deep breaths, coughing, or laughing.
* Bronchitis, pneumonia, and other lung infections occur often and keep coming back.
* Tiredness
* Unexplained weight loss
For Ovarian Cancer
These 4 symptoms last almost daily for longer than a few weeks:
* Bloating or swelling of the abdomen
* Pain in the upper abdomen or pelvic pressure
* Trouble eating or feeling full quickly
* Urgent need to urinate or urinating often
For Prostate Cancer
Early prostate cancer often does not cause symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include:
* Problems urinating
* Blood in the urine or semen
* Pain in the lower back, hips, ribs, or upper thighs
* Trouble having or keeping an erection
* Weakness or numbness in the feet or legs
For Testicular Cancer
* A lump on either testicle or surrounding area
* An enlarged testicle
* A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
* A dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin
* Sudden build-up of fluid in the scrotum
* Pain or discomfort in a testicle or the scrotum
* Enlarged or tender breasts
These symptoms could also be caused by other problems, such as infection or trauma of the scrotum or testicle from being hit or kicked. See your doctor if any of these symptoms lasts 2 weeks or longer. Males who are 15 and older should do a testicular self-exam if and as often as their doctors advise. Results are best after a warm bath or shower, which relaxes the scrotum, allowing the testicles to drop down for easier examination.
For Throat Cancer
* A sore in the mouth that does not heal
* Numbness of the tongue or other mouth area
* Pain in the mouth or bad breath that persists. A sore throat or a feeling that something is caught in the throat. This doesn’t go away.
* A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, tonsil, or lining of the mouth
* Hoarseness or other changes in the voice
* Lump or mass in the neck or cheek or a feeling of a lump in the throat
* Pain in the front of the neck, sometimes going up to the ears
* Trouble chewing or swallowing or moving the jaw or tongue.
* A cough that doesn’t go away
* Pressure, fullness, or burning sensations as food goes down the throat
* Upset stomach, heartburn, vomiting, and choking on food
* Unexplained weight loss
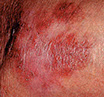
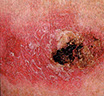
Basal and Squamous Cell Cancers
* Basal cell. More than 90% of all skin cancers in the U.S. are this type. It grows slowly. It seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
* Squamous cell. This type of skin cancer spreads more often than the basal cell type. It is still rare for it to spread, though.
Basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, like the head, face, neck, hands, and arms. These skin cancers can occur anywhere, though.
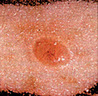
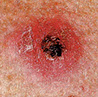
Early Warning Signs of Basal and Squamous Cell Cancers
Small, smooth, shiny, pale, or waxy lump.
A lump that bleeds or develops a crust.
A flat, red spot that is rough, dry, or scaly.
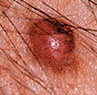
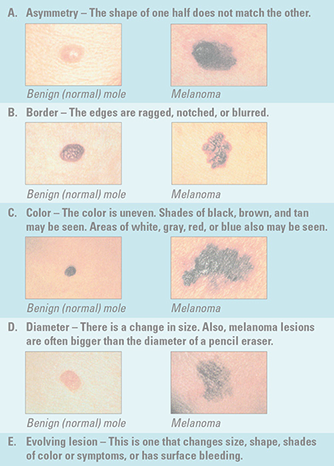
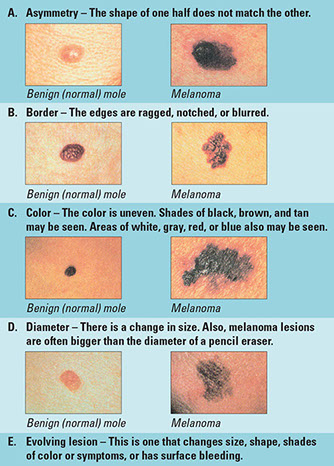
Warning Signs of Melanoma
This type of skin cancer can spread to other parts of the body and be fatal if not treated early. Often, the first sign is a change in the size, shape, or color of an existing mole. It also may appear as a new, abnormal, or “ugly looking” mole. Learn the ABCD and E’s that can help you detect it early.
Skin Self-Exam
* Do an exam monthly, after a shower or bath. To check your skin, use:
– A well-lit room
– A full-length mirror
– A hand-held mirror
* Locate your birthmarks, moles, and blemishes. Check for a change in the size, texture, or color of a mole. Check for a sore that does not heal.
Check all areas.
1. Look at the front and back of your body in the mirror. Raise your arms and look at your left and right sides.
2. Bend your elbows and look carefully at the palms of your hands. Look at both sides of your forearms and upper arms.
3. Look at the back and front of your legs. Look between the buttocks and around the genital area.
4. Sit and closely examine your feet. Look at the soles and between the toes.
5. Look at your face, neck, and scalp. Use a comb to move your hair so you can see your scalp.
See your doctor if you find anything unusual.
Causes & Risk Factors
With all cancers, genes that control cell growth and division malfunction. Damage to genes can occur from many factors.
Factors that damage genes include:
* Tobacco use and exposure
* Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun and indoor tanning
* Exposure to cancer causing chemicals
* A person’s genetic makeup and immune status
* Use of certain medicines, such as DES (a synthetic estrogen)
* Certain viruses and bacteria:
– Human papillomavirus (HPV). This causes most cervical cancers and some vaginal and vulvar cancers.
– Hepatitis B virus (HBV). This raises the risk for liver cancer.
– Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This raises the risk for some cancers, such as Kaposi sarcoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
– Helocobactor pylori (H. pylori) bacteria, the main cause of stomach ulcers, raises the risk for stomach cancer.
Lower Your Risk
There are many things you can do to prevent and lower your risk of getting cancer. Do them for yourself. Do them for your loved ones.
* Protect yourself from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Limit time in the sun. Wear sunscreen, sunglasses, a hat, and clothing that protects your skin. And, don’t fake bake. Sun lamps and tanning booths also emit cancer-causing rays.
* Have X-rays only when necessary.
* Avoid asbestos, pesticides, herbicides, and other cancer-causing agents. Protect yourself from cancer-causing chemicals at work and elsewhere.
* Have your home tested and treated for radon, if found.
* Do regular physical activity. Control your weight.
* Eat healthy foods. Have 5-9 colorful fruits and vegetables per day. Opt for whole-grain breads and cereals. Limit red meat and foods high in fat.
* Limit alcohol -no more than two drinks per day for men; no more than one drink per day for women.
* Find ways to manage stress. Too much stress can weaken your immune system.
* Talk with your doctor about taking vitamins, herbal products, or other supplements.
* Follow your doctor’s advice to prevent, lower the risk, and treat virus and bacteria that can cause cancer.
* The obvious – avoid tobacco:
– Don’t smoke it.
– Don’t shove it between your lips and gums.
– Don’t inhale it secondhand.
– Avoid thirdhand smoke – tobacco toxins that linger in carpets, clothes, furniture, and other materials hours or even days after a cigarette is put out.
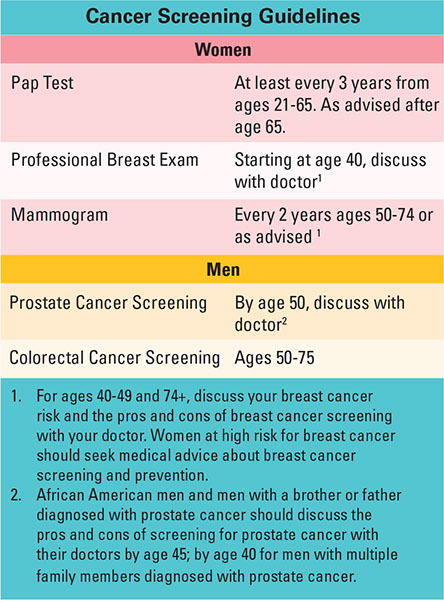
Screening Tests & Treatments
Screening tests help detect some types of cancer in early stages, when they are most treatable.
Finding and removing precancerous tissue can prevent cancers of the cervix, colon, and rectum.
Get screening tests, as listed below, or as advised by your doctor. If you are at a greater risk for one or more cancers, you may need screenings earlier or more often. You may need additional screenings. If a certain type of cancer is common in your family, consider asking your doctor about genetic testing. Also, check with your insurance plan to find out if and when screening tests are covered.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of cancer, the stage it is in, and individual factors. Cancer treatment includes:
* Surgery to remove the cancerous tumor(s) and clear any obstruction to vital passageways
* Radiation therapy
* Chemotherapy
* Biological therapy
* Targeted therapy, such as drugs, that affect only the cancer cells
* Stem cell or bone marrow transplant
* Clinical trials
Resources
American Cancer Society
800.ACS.2345 (227.2345)
www.cancer.org
National Cancer Institute
800.4.CANCER (422.6237)
www.cancer.gov
Clinical Trials
www.clinicaltrials.gov