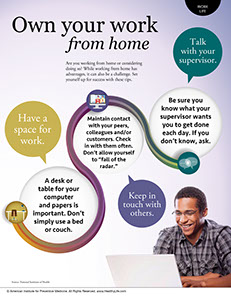
WORK LIFE

Work meetings are an opportunity to collaborate, share information, and strengthen connections. But, a poorly run meeting drains time and energy. Here’s how to make your meetings productive and worthwhile.
Have an agenda
Know exactly what needs to be addressed and put it in writing ahead of time. Try to stay on-topic and work your way through the planned agenda. If someone brings up something off-topic, plan another avenue to address it.
Be on time
Starting and ending as scheduled shows your employees and co-workers you value their time. Don’t wait for late arrivals, and don’t spend time bringing people up to speed if they arrive late. If you embrace a culture of punctuality, people will honor it.
Keep meetings small
Only invite the necessary people. A good general cap is 7-9 people, though your number will depend on your team. Smaller meetings allow everyone to participate and keep only the essential people involved.
Facilitate the discussion
As the meeting leader, it’s up to you to keep the conversation productive and on-task. Refer to the pre-planned agenda as needed to re-focus the discussion. If one person is dominating the talk, it’s OK to politely redirect.
Set clear action-items
A productive meeting should produce clear next steps to address the agenda items. End the session by restating the action items and clarifying who is responsible for each. Everyone should leave knowing what comes next.
Send follow-up details
Put the action items in writing and send them to the team to ensure everyone is on the same page. Be sure to follow up on anything that arose during the meeting. It will be easier for everyone to stay focused if they know you will follow through.